Opportunities, challenges, and requirements for Artificial Intelligence (AI) implementation in Primary Health Care (PHC): a systematic review
- PMID: 40490689
- PMCID: PMC12147259
- DOI: 10.1186/s12875-025-02785-2
Opportunities, challenges, and requirements for Artificial Intelligence (AI) implementation in Primary Health Care (PHC): a systematic review
Abstract
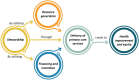
Background: Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly reshaped Primary Health Care (PHC), offering various possibilities and complexities across all functional dimensions. The objective is to review and synthesize available evidence on the opportunities, challenges, and requirements of AI implementation in PHC based on the Primary Care Evaluation Tool (PCET).
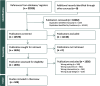
Methods: We conducted a systematic review, following the Cochrane Collaboration method, to identify the latest evidence regarding AI implementation in PHC. A comprehensive search across eight databases- PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Science Direct, Embase, CINAHL, IEEE, and Cochrane was conducted using MeSH terms alongside the SPIDER framework to pinpoint quantitative and qualitative literature published from 2000 to 2024. Two reviewers independently applied inclusion and exclusion criteria, guided by the SPIDER framework, to review full texts and extract data. We synthesized extracted data from the study characteristics, opportunities, challenges, and requirements, employing thematic-framework analysis, according to the PCET model. The quality of the studies was evaluated using the JBI critical appraisal tools.
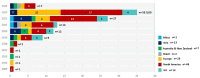
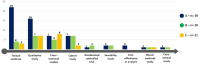
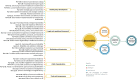
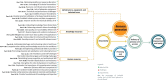
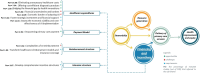
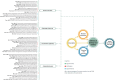
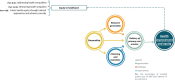
Results: In this review, we included a total of 109 articles, most of which were conducted in North America (n = 49, 44%), followed by Europe (n = 36, 33%). The included studies employed a diverse range of study designs. Using the PCET model, we categorized AI-related opportunities, challenges, and requirements across four key dimensions. The greatest opportunities for AI integration in PHC were centered on enhancing comprehensive service delivery, particularly by improving diagnostic accuracy, optimizing screening programs, and advancing early disease prediction. However, the most challenges emerged within the stewardship and resource generation functions, with key concerns related to data security and privacy, technical performance issues, and limitations in data accessibility. Ensuring successful AI integration requires a robust stewardship function, strategic investments in resource generation, and a collaborative approach that fosters co-development, scientific advancements, and continuous evaluation.
Conclusions: Successful AI integration in PHC requires a coordinated, multidimensional approach, with stewardship, resource generation, and financing playing key roles in enabling service delivery. Addressing existing knowledge gaps, examining interactions among these dimensions, and fostering a collaborative approach in developing AI solutions among stakeholders are essential steps toward achieving an equitable and efficient AI-driven PHC system.
Protocol: Registered in Open Science Framework (OSF) ( https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/HG2DV ).
Keywords: AI in Health; AI in PHC; AI in Primary Health Care; Artificial Intelligence; Primary Health Care; Systematic review.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This paper synthesizes evidence from other published studies; thus, ethics approval was not required. Consent for publication: No datasets were generated or analyzed for this study, so consent for publication does not apply. Competing of interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
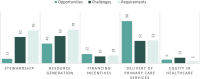
References
-
- Mehrolhassani MH, Dehnavieh R, Haghdoost AA, Khosravi S. Evaluation of the primary healthcare program in Iran: a systematic review. Aust J Prim Health. 2018;24(5):359–67. - PubMed
-
- Mathur MR. Revitalizing Alma-Ata: Strengthening primary oral health care for achieving universal health coverage. Indian J Dent Res. 2019;30:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Primary Health Care: Transforming Vision into Action: Operational Framework: Geneva: World Health Organization and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF); 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240017832.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
