Effects of dexmedetomidine and sevoflurane on optic nerve sheath diameter and postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing microvascular decompression: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 40490698
- PMCID: PMC12147279
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-025-03147-2
Effects of dexmedetomidine and sevoflurane on optic nerve sheath diameter and postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing microvascular decompression: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Observe the effects of dexmedetomidine(Dex) and sevoflurane(Sev) on the optic nerve sheath diameter(ONSD) in patients undergoing microvascular decompression (MVD). Find the most appropriate anesthetic maintenance medication scheme to reduce intracranial pressure (ICP)fluctuation and reduce the incidence of adverse reactions such as postoperative nausea and vomiting(PONV).
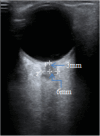
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, 90 patients undergoing elective MVD surgery were allocated into Groups P, D, and S. Maintenance of anaesthesia: Group P propofol(Propo) 4-12mg/(kg.h) + remifentanil 0.1-0.2ug/(kg.min); Group D Dex 0.4ug/(kg. h) + Propo 4-12mg/(kg.h) + remifentanil 0.1-0.2ug/(kg.min); Group S 1-2% Sev + Propo 4-12mg/(kg.h) + remifentanil 0.1-0.2ug/(kg.min). The changes in ultrasound-measured ONSD relative to baseline and the occurrence of PONV at different time periods under different anaesthetic maintenance regimens were compared.
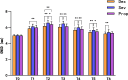
Results: (1) ONSD values increased significantly from T1 (10 min after tracheal intubation) to T6 (on leaving the post-anaesthesia care unit (PACU)), compared with the same group at T0 (5 min before anaesthesia). ONSD values at each time point of T1-T6, were the lowest in the Group D and the highest in the Group S.(2)In this study, the incidence of PONV within 24 h after MVD was 38.9%, with the lowest in Group D and the highest in Group S. (3) T2 (10 min after lying on side in forward neck flexion)ONSD, T6 (on leaving the PACU)ONSD, the usage of Sev and Dex were associated with PONV, whereas the usage of 0.4ug/(kg.h) Dex was a protective factor.
Conclusions: Dex has a lower effect on ONSD of MVD during the perioperative phase than Sev, and it can, to a certain extent, reduce the fluctuation of ICP. Dex lowers the incidence of PONV within 24 h after MVD and acts as a protective factor for PONV.
Trial registration: The protocol of this study was registered at www.chictr.org.cn (07/02/2024,ChiCTR MR-50-24-010856).
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine(Dex); Microvascular decompression(MVD); Optic nerve sheath diameter(ONSD); Postoperative nausea and vomiting(PONV); Sevoflurane(Sev).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Army Medical Center of PLA (No.10 ChangjiangZhilu, Yuzhong District, Chongqing 400042, China) on February 7, 2024, Ethics Registration No was 2024-Research-14. The study complied with the ethical standards set out in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. An approval for exemption of patients from informed consent was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Army Medical Center of PLA, which we can upload if required. This study has been registered at https://www.chictr.org.cn/ (07/02/2024,ChiCTR MR-50–24-010856). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of dexmedetomidine and esketamine for postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery: study protocol for a prospective, randomized, controlled trial.Trials. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13063-025-08935-2. Trials. 2025. PMID: 40598630 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sevoflurane versus other general anaesthesia on emergence agitation in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Sep 12;2014(9):CD007084. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007084.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25212274 Free PMC article.
-
Choice of Anesthetic for Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery Can Reduce the Use of Rescue Antiemetics in Postanesthesia Recovery Room: A Retrospective Observational Study.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2025 Apr 1;35(2):e1341. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000001341. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2025. PMID: 40063267
-
Intravenous versus inhalational maintenance of anaesthesia for postoperative cognitive outcomes in elderly people undergoing non-cardiac surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 21;8(8):CD012317. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012317.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30129968 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of obesity on optic nerve sheath diameter in patients undergoing laparoscopic gynecological surgery: a prospective observational study.J Anesth. 2025 Jun;39(3):408-415. doi: 10.1007/s00540-025-03482-1. Epub 2025 Mar 20. J Anesth. 2025. PMID: 40111534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolff Fernandes F, Krauss JK. Microvascular Decompression: A Bibliometric Analysis of the 100 Most Cited Articles. World Neurosurg. 2022;164:e67–81. 10.1016/j.wneu.2022.03.128. (Epub 2022 Apr 15 PMID: 35436582). - PubMed
-
- Yue Y, Zhao ZR, Liu DC, et al. Life-threatening complications after microvascular decompression procedure: Lessons from a consecutive series of 596 patients. J Clin Neurosci. 2021;86:64–70. 10.1016/j.jocn.2021.01.014. (Epub 2021 Jan 29 PMID: 33775349). - PubMed
-
- Hou Y, Liang H, Fan C, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine and postoperative nausea and vomiting after microvascular decompression surgery. J Clin Neurosci. 2023;116:27–31. 10.1016/j.jocn.2023.08.010. (Epub 2023 Aug 18 PMID: 37597331). - PubMed
-
- Mona R, Davood O, Alireza Z, et al. Effects of Dexmedetomidine On the Postoperative Shivering, Nausea, and Vomiting Among Opium User Patients Undergoing Elective Supratentorial Brain Tumor Surgery: A Randomized, Placebo Controlled Clinical trials. Galen Med J. 2021;10:1–8 10.31661/gmj.v10i0.2146. PMID: 35845235; PMCID: PMC9250811. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang F, Xie D, Xu H, et al. The effects of remifentanil-propofol combined with dexmedetomidine on cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients after ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2022;23(1):192. 10.1186/s13063-022-06121-2. PMID:35241145;PMCID:PMC8895834. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CSTB2021TIAD-KPX0058/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- CSTB2021TIAD-KPX0058/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- CSTB2021TIAD-KPX0058/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- CSTB2021TIAD-KPX0058/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- CSTB2021TIAD-KPX0058/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- CSTB2021TIAD-KPX0058/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- CSTB2021TIAD-KPX0058/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- CSTB2021TIAD-KPX0058/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- 82300561/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82300561/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82300561/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82300561/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82300561/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82300561/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82300561/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82300561/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

