Piperacillin-Tazobactam-Induced Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
- PMID: 40491609
- PMCID: PMC12146439
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.83786
Piperacillin-Tazobactam-Induced Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
Abstract
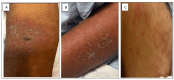
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is an extremely rare condition that is mostly caused by antibiotic exposure. Clinically, it manifests as the rapid appearance of multiple sterile pustules, swelling, and erythema within a few hours to days of exposure to the offending medication. Skin lesions usually resolve by desquamation after discontinuation of the offending agent. We present a case of a 58-year-old female patient with AGEP in the setting of piperacillin-tazobactam use, which was confirmed by histopathology with findings of neutrophilic pustules and eosinophilic infiltration. Her symptoms started resolving within three days of stopping the medication.
Keywords: acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; beta-lactam; beta-lactam antibiotics; cutaneous drug reaction; fever; piperacillin-tazobactam.
Copyright © 2025, Chapagain et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Piperacillin/Tazobactam as Cause of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis.Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2019 Apr 24;2019:3273987. doi: 10.1155/2019/3273987. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2019. PMID: 31179136 Free PMC article.
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: a rare clinical entity with use of piperacillin/tazobactam.Am J Ther. 2009 Nov-Dec;16(6):591-2. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e31818d5f6d. Am J Ther. 2009. PMID: 19352142
-
Piperacillin/Tazobactam-Associated Hypersensitivity Syndrome with Overlapping Features of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis and Drug-Related Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome.Ann Dermatol. 2016 Feb;28(1):98-101. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.1.98. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Ann Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 26848226 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis: Clinical Features, Differential Diagnosis, and Management.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Jul;24(4):557-575. doi: 10.1007/s40257-023-00779-3. Epub 2023 May 8. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37156992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical features, diagnosis and management of cephalosporin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Dec;47(12):2008-2013. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13738. Epub 2022 Jul 31. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 35909299
References
-
- Acute generalized exanthematic pustuloses (four cases) (author's transl) Beylot C, Bioulac P, Doutre MS. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6989310/ Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1980;107:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Results of patch testing in acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): a literature review. de Groot AC. Cont Dermat. 2022;87:119–141. - PubMed
-
- Moore MJ, Sathe NC, Ganipisetti VM. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. - PubMed
-
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. [ May; 2024 ]. 2023. https://www.aaaai.org/allergist-resources/ask-the-expert/answers/2023/ex... https://www.aaaai.org/allergist-resources/ask-the-expert/answers/2023/ex...
-
- Drug rashes: mild to moderate. [ Apr; 2024 ]. 2021. https://www.pcds.org.uk/clinical-guidance/adverse-cutaneous-drug-reactio... https://www.pcds.org.uk/clinical-guidance/adverse-cutaneous-drug-reactio...
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
