Consensus-based recommendations for indications and procedures in retinal laser treatment of Telangiectatic capillaries (TelCaps) in vascular macular oedema: A Delphi study
- PMID: 40492525
- PMCID: PMC12531603
- DOI: 10.1111/aos.17535
Consensus-based recommendations for indications and procedures in retinal laser treatment of Telangiectatic capillaries (TelCaps) in vascular macular oedema: A Delphi study
Abstract
Purpose: The identification of telangiectatic capillaries (TelCaps) in chronic macular oedema (ME) resistant to conventional intravitreal injections (IVIs) has renewed interest in focal laser treatment. However, the indications and modalities of this laser treatment remain to be clarified.
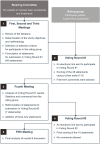
Methods: A modified Delphi approach was used to establish a consensus among French macular laser specialists regarding recommendations on assessment of TelCaps, indications for laser treatment, treatment procedures and follow-up.
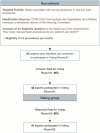
Results: Presence of TelCaps should be considered in cases of recurrent vascular oedema that do not respond, or partially respond, to IVIs. A strong consensus has emerged on treating TelCaps with laser when they are located ≥1000 μm from the fovea and associated with thickening of the surrounding retina, usually in combination with IVIs. For TelCaps located <1000 μm from the centre, IVIs alone were preferred. ICG-guided laser treatment was advised to target TelCaps but was not considered mandatory if TelCaps were visible on fundus photography or OCT. Assessment of the effectiveness of laser treatment should be based on reduction in macular thickness on OCT after 3 months, before a second laser session may be considered. Although experts have recommended the use of small, short-duration impacts allowing greying of the lesion, no consensus has been reached on the optimal numerical parameters for the laser procedure.
Conclusion: This study provides precise guidelines on laser treatment for vascular ME in cases of TelCaps, and emphasizes the need for standardized lesion selection and laser parameters to ensure safe and effective ME management.
Keywords: Delphi consensus macular oedema; TelCaps; diabetic retinopathy; focal laser photocoagulation; retinal vein occlusion; telangiectatic capillaries.
© 2025 The Author(s). Acta Ophthalmologica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
MN Delyfer: AbbVie, Bayer, Horus Pharma, Novartis, Roche, Thea. JF Girmens: AbbVie, Bayer, Biogen, Novartis, Roche, Teva, Tilak Healthcare. C Dot: AbbVie, Bayer, Horus Pharma, Novartis, Roche. M Bennani: None. MB Rougier: Abbvie, Bayer, Chiesi, Horus Pharma, Novartis. S Baillif: Abbvie, Alcon, Bausch and Lomb, Bayer, Biogen, Horus Pharma, Novartis, Roche. P Massin: Abbvie, Bayer, Novartis, Roche. V Gualino: Abbvie, Alcon, Bausch and Lomb, Bayer, Novartis, Roche. M Paques: SharpEye. B Dupas: Bayer, Novartis.
Figures
References
-
- AAO Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) Retina/Vitreous Panel, Hoskins Center for Quality Eye Care . (2023) Retina Summary Benchmarks. https://www.aao.org/education/summary‐benchmark‐detail/retina‐summary‐be...
-
- Allingham, M.J. , Mukherjee, D. , Lally, E.B. , Rabbani, H. , Mettu, P.S. , Cousins, S.W. et al. (2017) A quantitative approach to predict differential effects of anti‐VEGF treatment on diffuse and focal leakage in patients with diabetic macular edema: a pilot study. Translational Vision Science & Technology, 6, 7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avitabile, T. , Azzolini, C. , Bandello, F. , Boscia, F. , de Falco, S. , Fornasari, D. et al. (2017) Aflibercept in the treatment of diabetic macular edema: a review and consensus paper. European Journal of Ophthalmology, 27, 627–639. - PubMed
-
- Baker, C.W. , Glassman, A.R. , Beaulieu, W.T. , Antoszyk, A.N. , Browning, D.J. , Chalam, K.V. et al. (2019) Effect of initial management with Aflibercept vs laser photocoagulation vs observation on vision loss among patients with diabetic macular edema involving the Center of the Macula and Good Visual Acuity: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA, 321, 1880–1894. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blindbaek, S.L. , Peto, T. & Grauslund, J. (2019) How do we evaluate the role of focal/grid photocoagulation in the treatment of diabetic macular edema? Acta Ophthalmologica, 97, 339–346. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources