Nontargeted metabolomics analysis to unravel the anti-biofilm mechanism of Citrocin on Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 40492762
- PMCID: PMC12211082
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01628-24
Nontargeted metabolomics analysis to unravel the anti-biofilm mechanism of Citrocin on Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
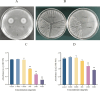
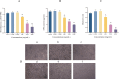
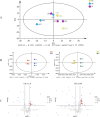
Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation is an important cause of cross-contamination in food processing. Citrinin is a potential broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptide. However, the effects of Citrocin on L. monocytogenes and its biofilm, as well as the associated mechanisms, remain to be explored. In this study, we evaluated the anti-biofilm effect of the antimicrobial peptide Citrocin on the foodborne pathogen L. monocytogenes and analyzed its anti-biofilm mechanism from the perspectives of swarming motility, extracellular polysaccharide production, and metabolite level changes. The results showed that Citrocin had a significant inhibitory effect on the growth of L. monocytogenes, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.075 mg/mL and a minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of 0.15 mg/mL. Citrocin at concentrations of MIC, 2 × MIC, and 4 × MIC could prevent biofilm formation and remove established biofilms. Metabolomics analysis revealed that Citrocin at 0.3 mg/mL caused a significant differential expression of metabolites in biofilms, up- and downregulating 23 and 13 metabolites, consisting mainly of amino acids, organic acids, and fatty acids, respectively. In addition, Citrocin significantly enriched energy and amino acid metabolic pathways, including alanine, glutamate, aspartate metabolism, TCA cycle, and arginine biosynthesis. This work provides potential biofilm regulation strategies and serves as a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of listeriosis.IMPORTANCEListeria monocytogenes biofilm formation is an important cause of cross-contamination during food processing. We found that Citrocin, an antimicrobial peptide that is widely used in animal feed, has good antimicrobial and anti-biofilm effects against L. monocytogenes. We preliminarily explored the anti-biofilm mechanism of Citrocin in terms of swarming motility, extracellular polysaccharide production, and metabolomics. Our work demonstrated that Citrocin is an excellent antimicrobial agent, which is important for the control of food cross-contamination and the preventive treatment of listeriosis.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes; biofilm; extracellular polysaccharide; metabolomics; swarming motility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Beyond antimicrobial resistance: MATE-type efflux pump FepA contributes to flagellum formation and virulence in Listeria monocytogenes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Jul 23;91(7):e0046225. doi: 10.1128/aem.00462-25. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40492698 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Composition of Toona sinensis Extract and its Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Antioxidant Activities, with Antibacterial Mechanisms against Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19112.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025 Jun 10;80(3):133. doi: 10.1007/s11130-025-01369-w. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40493126
-
The Anti-Microbial Peptide Citrocin Controls Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms by Breaking Down Extracellular Polysaccharide.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 8;25(7):4122. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074122. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612931 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim YJ, Yu HH, Song YJ, Park YJ, Lee NK, Paik HD. 2021. Anti-biofilm effect of the cell-free supernatant of probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 121:107667. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107667 - DOI
-
- Di Ciccio P, Rubiola S, Panebianco F, Lomonaco S, Allard M, Bianchi DM, Civera T, Chiesa F. 2022. Biofilm formation and genomic features of Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated from meat and dairy industries located in Piedmont (Italy). Int J Food Microbiol 378:109784. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109784 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

