Lipid profile and safety of rosuvastatin monotherapy versus rosuvastatin plus ezetimibe in high risk coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40493305
- PMCID: PMC12151963
- DOI: 10.1186/s43044-025-00654-y
Lipid profile and safety of rosuvastatin monotherapy versus rosuvastatin plus ezetimibe in high risk coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Combining lipid-lowering agents may enhance outcomes in patients with high-risk coronary artery disease. While rosuvastatin is known to reduce LDL-C and cardiovascular events, the additional benefit of ezetimibe remains under investigation. This meta-analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety of RSV combined with EZ compared to RSV monotherapy in high-risk coronary artery disease.
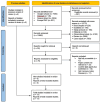
Methods: A systematic review was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar up to August 30, 2024. Data were analyzed using a random-effects model in Review Manager 5.4. Lipid profile and safety outcomes were assessed in accordance with PRISMA guidelines.
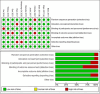
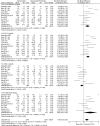
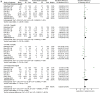
Results: Combination therapy with rosuvastatin and ezetimibe significantly improved the lipid profile in high-risk coronary artery disease patients compared to rosuvastatin monotherapy, based on 11 studies with 1,963 subjects. Treatment with RSV plus EZ decreased total cholesterol by 0.50 units (SMD = -0.50; 95% CI: -0.80 to -0.19; p = 0.001), LDL-C by 0.57 units (SMD = -0.57; 95% CI: -0.80 to -0.33; p < 0.00001), and triglycerides by 0.85 units (SMD = -0.85; 95% CI: -1.81 to -0.11; p = 0.002). Meanwhile, HDL-C increased by 0.26 units (SMD = 0.26; 95% CI: 0.04 to 0.48; p = 0.02). RSV monotherapy showed a significant risk of elevated liver enzymes (RR 0.36; 95% CI 0.13-0.99; p = 0.05), while combination therapy increased the risk of myalgia (RR 2.17; 95% CI 1.04-4.54; p = 0.04) and gastrointestinal symptoms (RR 2.00; 95% CI 1.01-3.97; p = 0.05). No significant difference in angina pectoris was noted (RR 0.84; 95% CI: 0.39-1.80; p = 0.65).
Conclusion: Combination therapy with RSV and EZ effectively improves lipid profiles in high-risk coronary artery disease patients, particularly in reducing total cholesterol, LDL-C, and triglycerides. However, it is associated with a higher risk of gastrointestinal symptoms and myalgia. In contrast, RSV monotherapy is linked to a greater risk of elevated liver enzymes but was also associated with increased HDL-C compared to the combination therapy of RSV + EZ.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Efficacy; Ezetimibe; Rosuvastatin; Safety.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Ballantyne CM, Weiss R, Moccetti T et al (2007) Efficacy and safety of rosuvastatin 40 mg alone or in combination with ezetimibe in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease (results from the EXPLORER study). Am J Cardiol 99(5):673–680. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2006.10.022 - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Zhao X, Li L, Yao H, Jiang Y, Zhang JY (2016) Effects of combination of ezetimibe and rosuvastatin on coronary artery plaque in patients with coronary heart disease. Heart Lung Circ 25(5):459–465 - PubMed
-
- Masuda J, Tanigawa T, Yamada T et al (2015) Effect of Combination Therapy of Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin on Regression of Coronary Atherosclerosis in Patients With coronary artery disease. Int Heart J 56:278–285 - PubMed
-
- Ran D, Nie H, juan, Gao Y lin, et al (2017) A randomized, controlled comparison of different intensive lipid-lowering therapies in Chinese patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS): Ezetimibe and rosuvastatin versus high-dose rosuvastatin. Int J Cardiol 235:49–55. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.02.099 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
