Kidney-specific WNK1 amplifies kidney tubule responsiveness to potassium via WNK body condensates
- PMID: 40493421
- PMCID: PMC12321387
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI188792
Kidney-specific WNK1 amplifies kidney tubule responsiveness to potassium via WNK body condensates
Abstract
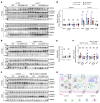
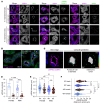
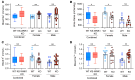
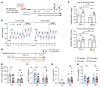
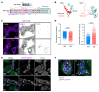
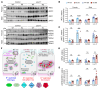
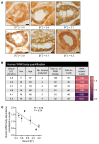
To maintain potassium homeostasis, the kidney's distal convoluted tubule (DCT) evolved to convert small changes in blood [K+] into robust effects on salt reabsorption. This process requires NaCl cotransporter (NCC) activation by the with-no-lysine (WNK) kinases. During hypokalemia, the kidney-specific WNK1 isoform (KS-WNK1) scaffolds the DCT-expressed WNK signaling pathway within biomolecular condensates of unknown function termed WNK bodies. Here, we show that KS-WNK1 amplified kidney tubule reactivity to blood [K+], in part via WNK bodies. In genetically modified mice, targeted condensate disruption trapped the WNK pathway, causing renal salt wasting that was more pronounced in females. In humans, WNK bodies accumulated as plasma potassium fell below 4.0 mmol/L, suggesting that the human DCT experiences the stress of potassium deficiency, even when [K+] is in the low-to-normal range. These data identify WNK bodies as kinase signal amplifiers that mediate tubular [K+] responsiveness, nephron sexual dimorphism, and BP salt sensitivity. Our results illustrate how biomolecular condensate specialization can optimize a mammalian physiologic stress response that impacts human health.
Keywords: Cell biology; Epithelial transport of ions and water; Molecular biology; Nephrology; Protein kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
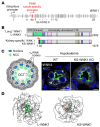
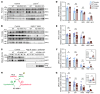
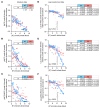
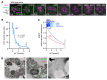
Comment in
- KS-WNK1 augments the effects of dietary potassium intake on renal sodium chloride reabsorption doi: 10.1172/JCI195512
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 DK137329/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD021627/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125439/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145875/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028596/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD036205/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL152680/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL155777/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119252/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK138215/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK111542/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK110358/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK118211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098145/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

