Protocol for the measurement of secreted acetylcholine in the lumen of mouse intestine using LC-MS
- PMID: 40493451
- PMCID: PMC12181018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.103848
Protocol for the measurement of secreted acetylcholine in the lumen of mouse intestine using LC-MS
Abstract
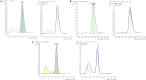
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a small-molecule neurotransmitter that regulates a wide range of neuronal and non-neuronal physiological functions. The non-neuronal roles of ACh are highly tissue specific, requiring precise measurements of its concentration in situ. Here, we present a protocol for measuring secreted ACh in the lumen of the mouse intestine. We describe the procedures for sample collection, preparation, and metabolite purification. Finally, we detail the use of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to quantify ACh levels. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Ndjim et al.1.
Keywords: Immunology; Metabolomics; Neuroscience.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ndjim M., Gasmi I., Herbert F., Joséphine C., Bas J., Lamrani A., Coutry N., Henry S., Zimmermann V.S., Dardalhon V., et al. Tuft cell acetylcholine is released into the gut lumen to promote anti-helminth immunity. Immunity. 2024;57:1260–1273.e7. - PubMed
-
- Dolan J.W. The role of the signal-to-noise ratio in precision and accuracy. LC-GC Eur. 2006;19:12–16.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

