A goat experimental epistaxis model: Hemostatic effect of stop nosebleeds device
- PMID: 40493637
- PMCID: PMC12151359
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324727
A goat experimental epistaxis model: Hemostatic effect of stop nosebleeds device
Abstract
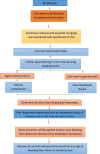
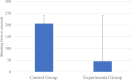
To stop epistaxis, a Saudi medical invention called "Stop Nosebleeds" with a patent was created. It is a silicone-based, adjustable device that is applied externally to the bridge of the nose and speeds up clotting by decreasing the temperature and the compressing effect of the device on the nose This study aims to examine the efficacy of the device in attaining hemostasis in goats with anterior nasal bleeding. An animal experimental nasal-bleeding model was conducted on ten goats in collaboration between King Fahad Medical City and King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The left nostril was used as interventional wounds and the right nostril was used as control. Control wounds were treated with manual compression for 20 minutes. Interventional wounds were treated with the Stop Nosebleeds device. The second group of animals was heparinized and 2 wounds were created in each animal, one of which was being treated with the Stop Nosebleeds device, while the other was being treated with manual compression. The mean bleeding duration in the experimental group (both heparinized and non-heparinized goats) was 45.5 seconds (SD = 8.2), compared to 206.0 seconds (SD = 75.7) in the control group (U = 0.00, p < 0.001). The device stopped bleeding in 52.0 seconds and 39.0 seconds in the heparinized and non-heparinized experimental groups. While, the manual compression of epistaxis stopped bleeding in 252.5 seconds (SD = 84.7) and 159.2 seconds (SD = 15.7) in the heparinized and non-heparinized control groups, respectively. The device shows promise for clinical application, however, further research with larger sample sizes and human clinical trials are needed to validate its efficacy and safety. Additionally, the use of a goat model presents limitations in directly translating these results to human clinical practice, and these differences should be careful.
Copyright: © 2025 Abu-Shaheen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Ayesha Tabassom JJD. Epistaxis. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2025. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK435997/.
-
- Yeung WWY, Judd O. Reviving a Lost Art: Hot-water Irrigation Treatment for Intractable Epistaxis. An International Journal of Clinical Rhinology. 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

