F-BIAS: Towards a distributed national core facility for bioimage analysis
- PMID: 40493670
- PMCID: PMC12151432
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1013058
F-BIAS: Towards a distributed national core facility for bioimage analysis
Abstract
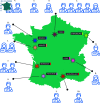
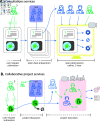
We discuss in this article the creation and organization of a national core facility for bioimage analysis, based on a distributed team. F-BIAS federates bioimage analysts across France and relies on them to deliver services to the researchers of this territory. The main challenge in implementing this structure is to ensure significant scientific value to the analysts, thereby encouraging their active participation and persuading their respective host teams to support their involvement. F-BIAS accomplished this by creating a professional network that mitigates the negative effects of isolation experienced by its members, who are often the sole bioimage analyst within their local teams, and fosters the development of their technical skills. In a second phase we capitalized on F-BIAS to create a virtual, remotely-operating core facility for bioimage analysis, offering consultations and collaborative project services to the scientific community of France. The services are organized so that they also contribute to the technical proficiency of the analysts. To promote the creation of similar structures, we present and discuss here the organization of this nationally distributed bioimage analysis service core, highlighting successes and challenges.
Copyright: © 2025 Ambroset et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Miura K. A survey on bioimage analysis needs. Zenodo. 2015. https://zenodo.org/record/4648077
-
- Cimini B. Community efforts and tools for bringing AI into the biology lab. Zenodo. 2023. https://zenodo.org/records/8300930
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

