Isoleucine Binding and Regulation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus Threonine Dehydratase (IlvA)
- PMID: 40494512
- PMCID: PMC12224302
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5c00168
Isoleucine Binding and Regulation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus Threonine Dehydratase (IlvA)
Abstract
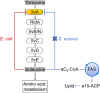
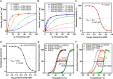
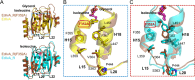
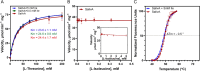
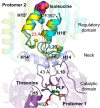
In Staphylococcus aureus, the branched-chain amino acid biosynthetic pathway provides essential intermediates for membrane biosynthesis. Threonine deaminase (IlvA) is the first enzyme in the pathway, and isoleucine feedback regulates the enzyme in Escherichia coli. These studies on E. coli IlvA (EcIlvA) introduced the concept of allosteric regulation. To investigate the regulation of S. aureus IlvA (SaIlvA), we first conducted additional studies on EcIlvA. The previously determined crystal structure of EcIlvA revealed a tetrameric assembly of protomers, each with catalytic and regulatory domains, but the structural basis of isoleucine regulation was not characterized. Here, we present the crystal structure of the EcIlvA regulatory domain bound to isoleucine, which reveals the isoleucine binding site and conformational changes that initiate at Phe352 and propagate 23 Å across the domain. This suggests an allosteric pathway that extends to the active site of the adjacent protomer, mediating regulation across the protomer-protomer interface. The EcIlvA(F352A) mutant binds isoleucine but is feedback-resistant due to the absence of the initiating Phe352. In contrast, SaIlvA is not feedback-regulated by isoleucine and does not bind it. The structure of the SaIlvA regulatory domain reveals a different organization that lacks the isoleucine binding site. Other potential allosteric inhibitors of SaIlvA, including phospholipid intermediates, do not affect enzyme activity. We propose that the absence of feedback inhibition in SaIlvA is due to its role in membrane biosynthesis. These findings enhance our understanding of IlvA's allosteric regulation and offer opportunities for engineering feedback-resistant IlvA variants for biotechnological use.
Figures





Update of
-
Isoleucine binding and regulation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus threonine dehydratase (IlvA).bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 28:2025.03.06.641827. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.06.641827. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Biochemistry. 2025 Jul 1;64(13):2793-2810. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5c00168. PMID: 40093177 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Isoleucine binding and regulation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus threonine dehydratase (IlvA).bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 28:2025.03.06.641827. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.06.641827. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Biochemistry. 2025 Jul 1;64(13):2793-2810. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5c00168. PMID: 40093177 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Structural and functional investigation of DinG containing a 3'-5' exonuclease domain.mBio. 2025 Aug 13;16(8):e0088425. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00884-25. Epub 2025 Jun 30. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40586552 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient approach to identify ilvA mutations reveals an amino-terminal catalytic domain in biosynthetic threonine deaminase from Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(20):6605-13. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.20.6605-6613.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8407838 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to reduce harm from continued tobacco use.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 13;10(10):CD005231. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005231.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27734465 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

