Loss of RNF41 promotes bladder cancer metastasis through increasing NUDC stability to enhance tubulin polymerization
- PMID: 40494872
- PMCID: PMC12152122
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07758-y
Loss of RNF41 promotes bladder cancer metastasis through increasing NUDC stability to enhance tubulin polymerization
Abstract
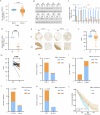
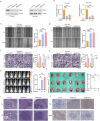
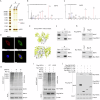
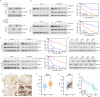
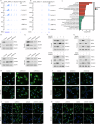
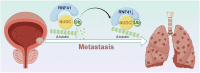
Bladder cancer (BCa) is a representative of urological cancer with a high recurrence and metastasis is the leading cause of death from BCa. The underlying mechanism of BCa metastasis remains poorly defined. Here, we found RNF41 was significantly downregulated in BCa tissue and low level of RNF41 is associated with BCa progression and poor prognosis. RNF41 knockdown promoted cell migration and invasion in both in vitro and in tail vein lung metastasis model, while ectopic RNF41 expression exhibited the opposite effects. Mechanically, we revealed that RNF41 directly interacted with NUDC and ubiquitinates NUDC to promote its degradation. Clinically, RNF41 was significantly downregulated in metastatic BCa tissues and negatively associated with NUDC expression. Furthermore, we identified that RNF41 promoted BCa lung metastasis through NUDC regulated β-tubulin depolymerization. In summary, these findings support that RNF41 was a tumor suppressor in BCa metastasis and highlights that targeting RNF41-NUDC-β-tubulin axis could be a valuable strategy to ameliorate BCa progression and metastasis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: The animal experiments performed here have been approved by the Animal Protection and Use Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University.
Figures

References
-
- Catto JWF, Gordon K, Collinson M, Poad H, Twiddy M, Johnson M, et al. Radical cystectomy against intravesical BCG for high-risk high-grade nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer: results from the randomized controlled BRAVO-feasibility study. J Clin Oncol J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2021;39:202–14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Grant No. 82460547/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- Grant No. 82172921/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- Grant No. 82460497/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- Grant No. 82203365/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- Grant No. 20242BAB26142/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Jiangxi Province Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

