LncRNA MIR99AHG serves as a diagnostic marker for early lung cancer and regulates cancer cell growth and metastasis via miR-194-5p
- PMID: 40495005
- PMCID: PMC12151976
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02896-3
LncRNA MIR99AHG serves as a diagnostic marker for early lung cancer and regulates cancer cell growth and metastasis via miR-194-5p
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer ranks among the foremost causes of mortality associated with cancer. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) represents the predominant subtype, and the survival rate is suboptimal.
Objectives: This study investigated the clinical relationship between MIR99AHG and NSCLC, as well as elucidated the potential mechanisms. This study identified novel molecular targets for NSCLC.
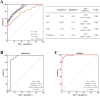
Patients and methods: This study involved 119 NSCLC patients and 105 benign lung lesions patients. qPCR was employed to assess the expression of MIR99AHG and miR-194-5p. The clinical correlation, diagnostic value, and predictive capacity of MIR99AHG were evaluated utilizing chi-square tests, ROC analysis, and logistic regression models, respectively. A cell model exhibiting overexpression of MIR99AHG was established, and the impact of MIR99AHG overexpression, and in conjunction with miR-194-5p overexpression, on the functional characteristics of lung cancer cells was investigated through CCK-8 and Transwell assays.
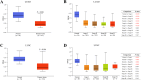
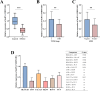
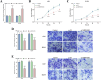
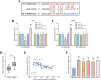
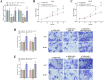
Results: MIR99AHG exhibited down-regulation in NSCLC patients' serum and lung cancer cell lines, while miR-194-5p showed up-regulation. The expression of MIR99AHG was correlated with TNM staging and LNM status in early-stage NSCLC patients. MIR99AHG demonstrated predictive capabilities for the early NSCLC occurrence, both independently and in conjunction with serum tumor markers, and exhibited significant diagnostic potential for this condition. Moreover, the overexpression of MIR99AHG could inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells. However, the concurrent overexpression of MIR99AHG and miR-194-5p appeared to negate this inhibitory effect.
Conclusion: MIR99AHG might as a supplementary diagnosis tool for early NSCLC. Furthermore, MIR99AHG could regulate the initiation and advancement of NSCLC via miR-194-5p.
Keywords: Cell function; Diagnosis; LncRNA; Non-small cell lung carcinoma; miRNA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. Ethical approval: The study has received approval from the Ethics Committee of Tengzhou Central People’s Hospital, and all experimental protocols have undergone ethical review. This research is conducted in strict accordance with the ethical guidelines outlined in the Helsinki Declaration established by the World Medical Association, as well as the Ethical Review Measures for Biomedical Research Involving Human Subjects set forth by the National Health Commission. Consent to participate: All participants have provided written informed consent, and the research protocol has thoroughly elucidated their rights, potential risks, and the objectives of the study. Each participant has consented to engage in this research and to the publication of pertinent data. Consent to publish: Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MIR99AHG inhibits EMT in pulmonary fibrosis via the miR-136-5p/USP4/ACE2 axis.J Transl Med. 2022 Sep 23;20(1):426. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03633-y. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36138468 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MIR99AHG mediated by FOXA1 modulates NOTCH2/Notch signaling pathway to accelerate pancreatic cancer through sponging miR-3129-5p and recruiting ELAVL1.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Dec 15;21(1):674. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02189-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34911544 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the anti-tumor effects of midazolam in non-small cell lung cancer through the lncRNA XLOC_010706/miR-520d-5p/STAT3/autophagy pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 May 14;15(1):16796. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01625-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40369043 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00511 promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting miR-625-5p/GSPT1.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Dec;10(12):5159-5173. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1468. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116366 Free PMC article.
-
IncRNA EPB41L4A-AS1 Mitigates the Proliferation of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through the miR-105-5p/GIMAP6 Axis.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2023;33(2):27-40. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2022044323. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2023. PMID: 36734855
References
-
- Nojima T, Proudfoot NJ. Mechanisms of LncRNA biogenesis as revealed by nascent transcriptomics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23(6):389–406. 10.1038/s41580-021-00447-6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
