Wnt/β-catenin mediated signaling pathways in cancer: recent advances, and applications in cancer therapy
- PMID: 40495229
- PMCID: PMC12150590
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02363-1
Wnt/β-catenin mediated signaling pathways in cancer: recent advances, and applications in cancer therapy
Abstract
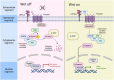
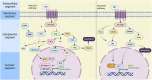
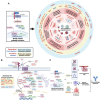
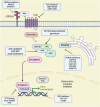
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is a highly conserved signaling pathway closely linked to cancer development through various biological processes, including oncogenic transformation, genomic instability, cancer cell proliferation, stemness, metabolism, cell death, immune regulation, and metastasis. Notably, its activation plays a crucial role in drug resistance to chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Recent advances in drug development have identified several targeted inhibitors acting at key nodal points of this pathway, with some demonstrating synergistic efficacy when combined with immunotherapeutic agents. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of current understanding regarding the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in malignancy, emphasizing its multifaceted roles in tumor initiation, therapeutic resistance, and immune regulation. Additionally, we summarized the clinical performance of combination therapies targeting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in conjunction with chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Although clinical development remains at a relatively early stage, pharmacological modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling offers considerable potential as a novel therapeutic paradigm in precision oncology.
Keywords: Cancer; Combined therapy; Immunotherapy; Targeted therapy; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent of publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in carcinogenesis and cancer therapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jun 18;17(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01563-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38886806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Dec 4;13(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00990-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33276800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Belling the "cat": Wnt/β-catenin signaling and its significance in future cancer therapies.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Nov;1879(6):189195. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189195. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39413855 Review.
-
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway: modulating anticancer immune response.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 May 5;10(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0471-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28476164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Versatile Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Cancer Biology and Therapeutics: From Concept to Actionable Strategy.OMICS. 2019 Nov;23(11):517-538. doi: 10.1089/omi.2019.0147. Epub 2019 Oct 15. OMICS. 2019. PMID: 31613700
Cited by
-
Harnessing the interaction between redox signaling and senescence to restrain tumor drug resistance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 9;13:1639772. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1639772. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40703657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of KIAA1429 promotes oxaliplatin resistance through activating the FZD7-Wnt signaling in BRAFV600E-mutated colorectal cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 3;44(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03449-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40611274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nusse R, et al. Varmus, Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982;31(1):99–109. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127(3):469–80. - PubMed
-
- He S, et al. WNT/β-catenin signaling in the development of liver cancers. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;132: 110851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

