Epigenome-wide association study of cerebrospinal fluid-based biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease in cognitively normal individuals
- PMID: 40495554
- PMCID: PMC12152373
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70318
Epigenome-wide association study of cerebrospinal fluid-based biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease in cognitively normal individuals
Abstract
Introduction: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease (AD) are reliable predictors of future AD risk. We investigated whether pre-clinical changes in AD CSF biomarkers are reflected in blood DNA methylation (DNAm) levels in cognitively normal participants.
Methods: We profiled blood-based DNAm with the EPIC array in participants without a diagnosis of cognitive impairment in the Emory Healthy Brain Study (EHBS; N = 495), Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (N = 122), and Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative (N = 118) cohorts. Their CSF amyloid beta 42, total tau (t-tau), and phosphorylated tau181 levels were quantified using Elecsys immunoassays. We conducted epigenome-wide association studies to assess associations between DNAm and CSF biomarkers of AD.
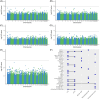
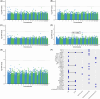
Results: In EHBS, no loci were Bonferroni significant after adjusting for confounding factors. In the meta-analysis of all three cohorts, DNAm in cg22976567 (LMNA) was significantly associated with higher CSF t-tau levels.
Discussion: Our study showed little evidence of an association between differential blood-based DNAm and pre-clinical AD CSF biomarkers.
Highlights: We conducted one of the largest (n = 735) blood DNA methylation (DNAm) studies of Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid (AD CSF) biomarkers. This is the first epigenome-wide association study in cognitively normal participants examining AD CSF biomarkers. Limited associations between blood DNAm and AD CSF biomarkers were identified.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; DNA methylation; amyloid; biomarker; blood; cerebrospinal fluid; epigenetics; epigenome‐wide association study.
© Published 2025. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
Update of
-
Epigenome-wide association study of cerebrospinal fluid-based biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease in cognitively normal individuals.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 5:2025.02.04.25321657. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.04.25321657. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jun;21(6):e70318. doi: 10.1002/alz.70318. PMID: 39974053 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Epigenome-wide association study of cerebrospinal fluid-based biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease in cognitively normal individuals.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 5:2025.02.04.25321657. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.04.25321657. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jun;21(6):e70318. doi: 10.1002/alz.70318. PMID: 39974053 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Distinct CSF biomarker-associated DNA methylation in Alzheimer's disease and cognitively normal subjects.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023 Apr 10;15(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01216-7. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37038196 Free PMC article.
-
Blood DNA methylomic signatures associated with CSF biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease in the EMIF-AD study.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Oct;20(10):6722-6739. doi: 10.1002/alz.14098. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39193893 Free PMC article.
-
The Associations of Phosphorylated Tau 181 and Tau 231 Levels in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid with Cognitive Function in Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;98(1):13-32. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230799. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38339929
-
Simultaneous analysis of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers using microsphere-based xMAP multiplex technology for early detection of Alzheimer's disease.Methods. 2012 Apr;56(4):484-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.03.023. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Methods. 2012. PMID: 22503777 Review.
References
-
- Xu J, Murphy SL, Kockanek KD, Arias E. Mortality in the United States, 2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2020;355:1‐6. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db355.htm. Available from. - PubMed
-
- 2021 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17(3):327‐406. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K. CSF biomarkers for mild cognitive impairment. J Intern Med. 2004;256(3):224‐234. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AG079170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- IK4 BX005219/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- IK4BX005219/Veterans Affairs
- P30 AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG088425/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG061356/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01BX003853/Veterans Affairs
- U01 AG046161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG079170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX005686/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- U01 AG061356/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG072120/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG056533/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003853/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01AG056533/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01BX005686/Veterans Affairs
- P30AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG072120/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG061357/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG070937/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG087250/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG087250/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG061357/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG046161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG070937/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG088425/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG075827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG075827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

