Effectiveness and safety of blonanserin monotherapy for first-episode schizophrenia with and without prominent negative symptoms: A prospective study
- PMID: 40495846
- PMCID: PMC12146995
- DOI: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i5.103701
Effectiveness and safety of blonanserin monotherapy for first-episode schizophrenia with and without prominent negative symptoms: A prospective study
Abstract
Background: Blonanserin, a novel antipsychotic, has demonstrated efficacy in treating both positive and negative symptoms. However, limited research exists on its dose-dependent effectiveness and safety in patients with and without prominent negative symptoms (PNS).
Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of blonanserin monotherapy for first-episode schizophrenia in real-world clinical settings and to explore the efficacy and safety of different doses of blonanserin for patients with PNS and without PNS.
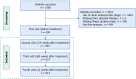
Methods: A 12-week, multicenter, prospective post-marketing surveillance was conducted. In this study, we included patients with first-episode schizophrenia who received blonanserin monotherapy. Patients were divided into those with PNS and without PNS, based on the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) negative symptoms subscale scores. Additionally, patients were labeled as high-dose and low-dose groups according to the maximum daily dose they received. Effectiveness was assessed using the BPRS, and safety was evaluated through the incidence of adverse drug reactions (ADRs).
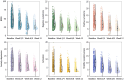
Results: A total of 653 patients were included in the analysis, with 613 completing the study. The BPRS total score decreased significantly from 47.94 ± 16.31 at baseline to 26.88 ± 9.47 at 12 weeks (P < 0.001). A significant interaction of PNS × dose × time was observed for BPRS total scores (F = 3.47, P = 0.040) and negative symptom subscale scores (F = 6.76, P = 0.002). In the PNS group, the high-dose group showed greater reductions in BPRS total scores (P = 0.001) and negative symptom subscale scores (P = 0.003) than the low-dose group in week 12. In the without PNS group, no significant difference was observed between the high-dose and low-dose groups at any visit. Most adverse reactions were mild or moderate, with extrapyramidal symptoms (9.3%) being most common; 1.5% of patients gained ≥ 7% body weight at 12 weeks.
Conclusion: Blonanserin effectively alleviated the clinical symptoms of first-episode schizophrenia with an acceptable safety profile. High-dose blonanserin is particularly beneficial for patients with PNS in the acute phase of first-episode schizophrenia. However, due to the limitation of ADR reporting the real world, the ADR incidence observed in this study may be underestimated.
Keywords: Blonanserin; Dose; Effectiveness; Negative symptoms; Safety; Schizophrenia.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and safety of blonanserin in young and middle-aged female patients with schizophrenia: data from a post-marketing surveillance.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Feb 21;23(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-04598-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36810039 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and effectiveness of oral medium to high dose blonanserin in patients with schizophrenia: subgroup analysis from a prospective, multicenter, post-marketing surveillance study in mainland China.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 6;22(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12991-023-00467-w. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37803378 Free PMC article.
-
Who can benefit more from its twelve-week treatment: A prospective cohort study of blonanserin for patients with schizophrenia.World J Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 19;14(11):1735-1745. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i11.1735. eCollection 2024 Nov 19. World J Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39564169 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and effectiveness of oral blonanserin for schizophrenia: A review of Japanese post-marketing surveillances.J Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Jan;145(1):42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2020.09.006. Epub 2020 Oct 8. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33357778 Review.
-
Long-term oral blonanserin treatment for schizophrenia: a review of Japanese long-term studies.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 7;20(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12991-021-00361-3. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34493318 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Velligan DI, Rao S. The Epidemiology and Global Burden of Schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2023;84:MS21078COM5. - PubMed
-
- Best MW, Law H, Pyle M, Morrison AP. Relationships between psychiatric symptoms, functioning and personal recovery in psychosis. Schizophr Res. 2020;223:112–118. - PubMed
-
- McCutcheon RA, Reis Marques T, Howes OD. Schizophrenia-An Overview. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77:201–210. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

