Xanthohumol ameliorates diabetic kidney disease through suppression of renal fibrosis by regulating SNHG10/miR-378b
- PMID: 40495890
- PMCID: PMC12149104
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532517
Xanthohumol ameliorates diabetic kidney disease through suppression of renal fibrosis by regulating SNHG10/miR-378b
Abstract
Content: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD), commonly termed diabetic nephropathy (DN), is characterized by oxidative stress and renal tubular epithelial cells apoptosis driven by high glucose (HG).
Objective: To explore the protective effects and underlying mechanism of xanthohumol in DN mice and HG-induced HK-2 cells.
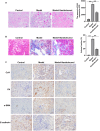
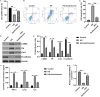
Materials and methods: The STZ-treated mice and HG stimulated HK-2 cells were applied to establish in vivo and in vitro DN models. The concentrations of blood glucose, serum creatinine, BUN and urine creatinine, and β-n-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG) activity was determined. The pathological changes of renal tissues were evaluated by Masson and periodic acid schiff (PAS) staining. TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 levels were detected using ELISA. Furthermore, CCK-8 assay and flow cytometer analysis were applied for determining HK-2 cells viability and apoptosis, respectively. Gene and protein levels was evaluated by qRT-PCR analysis and western blot/IHC. The relationship between lncRNA SNHG10 and miR-378b was confirmed by luciferase reporter assay.
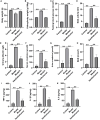
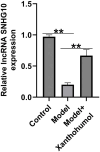
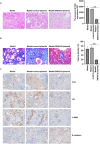
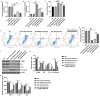
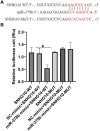
Results: Xanthohumol effectively improves DN-stimulated kidney structural and functional abnormalities. LncRNA SNHG10 was downregulated in the renal tissues of DN mice and HG induced HK-2 cells, while this inhibition was reversed by xanthohumol treatment. We also noted that xanthohumol remarkably reversed HG induced HK-2 cells injury. Upregulation of lncRNA SNHG10 also improved DN in mice. Meanwhile, downregulation of SNHG10 reversed the effects of xanthohumol on HG-induced HK-2 cells. Additionally, miR-378b directly targeted lncRNA SNHG10.
Conclusion and discussion: Xanthohumol inhibited the progression of DN by regulating SNHG10/miR-378b, indicating a novel understanding of xanthohumol in DN progression and providing a latent therapeutic target for DN therapy.
Keywords: SNHG10/miR-378b; diabetic nephropathy; inflammatory response; interstitial fibrosis; renal fibrosis; xanthohumol.
Copyright © 2025 Hao, Li and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
β-Amyrin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in mice and regulates the miR-181b-5p/HMGB2 axis in high glucose-stimulated HK-2 cells.Environ Toxicol. 2022 Mar;37(3):637-649. doi: 10.1002/tox.23431. Epub 2021 Dec 11. Environ Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34894065
-
Downregulation of Salusin-β protects renal tubular epithelial cells against high glucose-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and lipid accumulation via suppressing miR-155-5p.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):6155-6165. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1972900. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34482798 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-133a-3p Attenuates Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury via Targeting MALM1 and Suppressing the Notch Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Nephropathy.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):2401-2411. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01351-4. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38878099
-
LncRNA NEAT2 Modulates Pyroptosis of Renal Tubular Cells Induced by High Glucose in Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) by via miR-206 Regulation.Biochem Genet. 2022 Oct;60(5):1733-1747. doi: 10.1007/s10528-021-10164-6. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Biochem Genet. 2022. PMID: 35084640
-
Circ_0000064 promotes high glucose-induced renal tubular epithelial cells injury to facilitate diabetic nephropathy progression through miR-532-3p/ROCK1 axis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Mar 15;22(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-00968-x. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 35291991 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

