Low levels of adropin are associated with acute kidney injury after decongestion in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure
- PMID: 40496057
- PMCID: PMC12150235
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100302
Low levels of adropin are associated with acute kidney injury after decongestion in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure
Abstract
Background: Patients with acutely decompensated heart failure (ADHF) demonstrated a high risk of acute kidney injury (AKI) and its transition to acute kidney disease after diuretic therapy to reach euvolemic status. The purpose of the study was to investigate whether circulating levels of adropin predict AKI in ADHF patients after decongestive therapy.
Material and methods: A total of 325 individuals fulfilling the inclusion criteria of ADHF were consecutively enrolled from October 2020 to October 2024. The study was designed as prospective cohort study. The congestion was assessed using Framingham criteria of congestion (Framingham heart failure score ≥ 2). Patients with AHDF were divided into 2 groups according to the presence of AKI (n = 113) and without AKI (n = 212). Circulating levels of N-terminal brain natriuretic pro-peptide (NT-proBNP), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, high-sensitive troponin T, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity-2, procalcitonin were measured. Predictors of AKI were identified using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
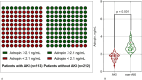
Results: We found that the presence of atrial fibrillation, urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (UACR) ≥16.5 mg/g Cr, serum levels of adropin<2.1 ng/mL and NT-proBNP ≥19,540 pmol/mL were independent predictors for AKI in patients with ADHF. UACR and atrial fibrillation revealed a strict similarity in prediction of AKI, whereas discriminative ability of adropin<2.1 ng/mL were higher to NT-proBNP ≥19,540 pmol/mL. The combined predictive model (low levels of adropin + higher levels of NT-proBNP) showed significantly better discriminatory power compared to other models.
Conclusion: Low levels of adropin<2.1 ng/mL on hospital admission in patients with ADHF can predict AKI and that its predictive ability was significantly higher compared with the conventionally used urinary albumin/creatinine ratio and NT-proBNP. Adropin may add predictive information to NT-proBNP for AKI in individuals with ADHF.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Acutely decompensated heart failure; Adropin; Biomarkers; Decongestion; Prognosis.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors for Irreversibility of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Obesity After Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography.Adv Ther. 2025 Jan;42(1):293-309. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-03036-z. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 39527336
-
Adropin Predicts Asymptomatic Heart Failure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Independent of the Levels of Natriuretic Peptides.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 9;14(16):1728. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14161728. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202216 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting acute kidney injury using urinary liver-type fatty-acid binding protein and serum N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels in patients treated at medical cardiac intensive care units.Crit Care. 2018 Aug 18;22(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2120-z. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30119691 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of acute kidney injury in patients with acute decompensated heart failure in emergency departments in China.J Int Med Res. 2021 Sep;49(9):3000605211016208. doi: 10.1177/03000605211016208. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34510958 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of plasma biomarkers in discharged heart failure patients: role of plasma NT-proBNP.Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016 Apr;64(2):157-64. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016. PMID: 26373781 Review.
References
-
- Limkunakul C., Srisantithum B., Lerdrattanasakulchai Y., Laksomya T., Jungpanich J., Sawanyawisuth K. Any heart failure treatments associated with worsening renal function in patients admitted due to acute heart failure? Ren Fail. 2021;43(1):123–127. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1858100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

