Triglyceride-glucose index in predicting gastric cancer prognosis: A need for caution
- PMID: 40496367
- PMCID: PMC12146930
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i18.104525
Triglyceride-glucose index in predicting gastric cancer prognosis: A need for caution
Abstract
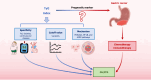
Gastric cancer (GC) remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Accurate prognostic assessment, which is essential for enhancing overall survival (OS), currently depends on pathologic and clinical staging. This underscores the urgent need for reliable and real-time prognostic biomarkers. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, a readily available marker of insulin resistance, has recently emerged as a potential prognostic tool in GC. Numerous studies have consistently shown a significant association between elevated TyG levels and inferior OS as well as progression-free survival. Despite these promising findings, several challenges must be addressed before the TyG index can be widely adopted in clinical practice. Firstly, the TyG index lacks cancer-specificity, reflecting broader metabolic disturbances commonly observed in conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. This lack of specificity complicates its interpretation in oncological settings. Additionally, the cutoff values for TyG index vary across studies, hindering the establishment of a standardized threshold for clinical application. While the TyG index provides valuable insights into a patient's metabolic health, its limited cancer specificity necessitates cautious use when evaluating the prognosis of GC treatment.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; Glycolipid metabolism; Overall survival; Prognostic biomarker; Progression-free survival; Triglyceride-glucose index.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Bentrem DJ, Chao J, Cooke D, Corvera C, Das P, Enzinger PC, Enzler T, Fanta P, Farjah F, Gerdes H, Gibson MK, Hochwald S, Hofstetter WL, Ilson DH, Keswani RN, Kim S, Kleinberg LR, Klempner SJ, Lacy J, Ly QP, Matkowskyj KA, McNamara M, Mulcahy MF, Outlaw D, Park H, Perry KA, Pimiento J, Poultsides GA, Reznik S, Roses RE, Strong VE, Su S, Wang HL, Wiesner G, Willett CG, Yakoub D, Yoon H, McMillian N, Pluchino LA. Gastric Cancer, Version 2.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2022;20:167–192. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM, Jemal A. Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates and Trends--An Update. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2016;25:16–27. - PubMed
-
- Kunz PL, Gubens M, Fisher GA, Ford JM, Lichtensztajn DY, Clarke CA. Long-term survivors of gastric cancer: a California population-based study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:3507–3515. - PubMed
-
- Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Almhanna K, Bentrem DJ, Chao J, Das P, Denlinger CS, Fanta P, Farjah F, Fuchs CS, Gerdes H, Gibson M, Glasgow RE, Hayman JA, Hochwald S, Hofstetter WL, Ilson DH, Jaroszewski D, Johung KL, Keswani RN, Kleinberg LR, Korn WM, Leong S, Linn C, Lockhart AC, Ly QP, Mulcahy MF, Orringer MB, Perry KA, Poultsides GA, Scott WJ, Strong VE, Washington MK, Weksler B, Willett CG, Wright CD, Zelman D, McMillian N, Sundar H. Gastric Cancer, Version 3.2016, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2016;14:1286–1312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

