Antioxidant strategies against cellular senescence: unveiling the power of synthetic versus natural antioxidants in a systematic review
- PMID: 40496803
- PMCID: PMC12149200
- DOI: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1543360
Antioxidant strategies against cellular senescence: unveiling the power of synthetic versus natural antioxidants in a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Cellular senescence, characterized by irreversible cell cycle arrest, plays a pivotal role in ageing and the development of age-related pathologies. Mitigating oxidative stress, a primary contributor to cellular ageing, is crucial for inhibiting the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). A comparative analysis of synthetic and natural antioxidants is necessary to evaluate the efficacy of synthetic and natural antioxidants in this context.
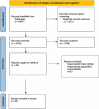
Method: A systematic review encompassed studies published up to July 2023, utilizing prominent databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science. To enhance the efficiency of data screening and selection, we employed Rayyan. ai, an advanced tool designed for systematic reviews.
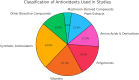
Result: The review encompassed 33 studies examining the impact of diverse antioxidants on cellular senescence. Findings indicated that synthetic antioxidants, such as N-acetylcysteine, and natural alternatives, like Vitamin C, demonstrated efficacy in attenuating oxidative stress and senescence markers. Notably, natural antioxidants frequently exhibited comparable or superior efficacy to their synthetic counterparts in most studies. Furthermore, the synergistic effects of antioxidant combinations sometimes yield enhanced benefits. It is worth noting that certain recently developed synthetic compounds, such as MHY2233, have shown promising results, exhibiting greater potency than established antioxidants in mitigating senescence markers.
Conclusion: Dietary practices and the aging process can influence these intricate processes and how they interact, serving as potential primary and secondary preventative strategies. The Mediterranean diet, dietary antioxidants, and limiting calorie intake are promising nutritional strategies. Better insight into the molecular mechanisms of aging may facilitate the development of efficient biomarkers and antioxidants for diagnosis or treatment.
Systematic review registration: https://osf.io/b67wm/.
Keywords: aging; antioxidants; cellular senescence; food-derived antioxidants; natural antioxidants.
Copyright © 2025 Ebrahimirad, Mirmahdizade, Mahmoodieh, Najafi, Banihashemian, Nikakhtar, Mobaraki, Sadeghi, Kossari, SadatRafiei, Ghodsi Moghadam, Mashkani, Asadi Anar and khosravi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Amarachukwu Uzombah T. (2022). “The implications of replacing synthetic antioxidants with natural ones in the food systems,” in Natural food additives.
-
- Atta E. M., Mohamed N. H., Abdelgawad A. A. M. (2017). Antioxidants: an overview on the natural and synthetic types. Eur. Chem. Bull. 6 (8), 365–375. 10.17628/ecb.2017.6.365-375 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources