Case Report: Robust and durable response to the combination of tislelizumab and chemotherapy in advanced thymic epithelial tumors: a case series
- PMID: 40496871
- PMCID: PMC12149142
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1516297
Case Report: Robust and durable response to the combination of tislelizumab and chemotherapy in advanced thymic epithelial tumors: a case series
Abstract
Background: Thymic epithelial tumors (TETs), categorized predominantly as thymoma (T) or thymic carcinoma (TC), face a challenging prognosis and limited treatment options. Although chemotherapy remains the established treatment for advanced TETs, its responses tend to be short-lived. The emergence of immunotherapy, particularly programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and programmed death ligand-1 inhibitors (PD-L1), is increasingly being regarded as a promising new treatment option for various malignancies.
Methods: Herein, we present a case series of eight patients with TETs who received tislelizumab treatment at Jiangsu Provincial Hospital between 2021 and 2023. All cases were histologically confirmed as either thymoma or thymic carcinoma. Among these eight cases, six patients (5 thymic carcinomas [TC] and 1 thymoma [T]) received tislelizumab in combination with chemotherapy following multiple cycles of prior chemotherapy without achieving significant therapeutic response. Two TC patients were administered this combination regimen as first-line treatment. Following the initiation of immunotherapy, patients received tislelizumab at a dose of 200 mg every three weeks until disease progression or the occurrence of unacceptable toxicity. Treatment response was assessed by the investigators according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1 guidelines.
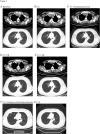
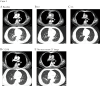
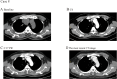
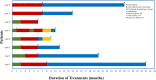
Results: The 8 patients described had a median age of 59 years (range, 47-72). During the course of immunotherapy, five patients (62.5%) achieved partial response, and notably, even after transitioning to maintenance therapy with tislelizumab, the lesions continued to shrink, with the longest sustained partial response lasting over 2 years. Three patient (37.5%) experienced stable disease as their best response to immunotherapy. Among all these patients, three patients (37.5%) demonstrated initial efficacy but subsequently exhibited progressive disease (median progression-free survival of 14 months). All patients are still being followed up, with the longest PFS extending to 31 months. Notably, five of the eight patients underwent PD-L1 testing and were all found to be negative. Despite this, no immune-related Grade 3-5 adverse events (AEs) were reported and all AEs were manageable with supportive measures. Grade 1-2 AEs were adrenal insufficiency (n=1), thyroid dysfunction (n=1), and pneumonia (n=1).
Conclusions: Our study findings suggest that the combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy yields durable clinical responses in patients with TETs, suggesting its potential as a safe and effective first-line treatment strategy for advanced TETs. Notably, the therapeutic benefits of chemo-immunotherapy appear to extend beyond patients with high PD-L1 expression (≥50%), indicating that this treatment approach may not be strictly limited to individuals with elevated PD-L1 levels.
Keywords: case report; first-line treatment; immunotherapy; thymic carcinoma; thymoma; tislelizumab.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Li, Wang, Yu, He and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined programmed cell death protein 1 and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 blockade in an international cohort of patients with acral lentiginous melanoma.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jan 24;192(2):316-326. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae401. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39438074
-
The efficacy and safety of tislelizumab with or without tyrosine kinase inhibitor as adjuvant therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma with high-risk of recurrence after curative resection.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1593153. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1593153. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40607378 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 combination therapy in first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC: an updated systematic review and network meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Oct;26(10):2488-2502. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03442-3. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38625495
-
Taxane monotherapy regimens for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7(7):CD008766. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008766.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866378 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

