Identification and Validation of Oxidative Stress-Related Diagnostic Marker Genes and Immune Landscape in Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis by Integrating Bioinformatics and Machine Learning
- PMID: 40497148
- PMCID: PMC12151081
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S524653
Identification and Validation of Oxidative Stress-Related Diagnostic Marker Genes and Immune Landscape in Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis by Integrating Bioinformatics and Machine Learning
Abstract
Purpose: Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic inflammatory disease with autoimmune associations, particularly in ulcerative IC, a severe and refractory subtype. Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in IC pathogenesis, interacting with inflammation and immune cell infiltration. This study aimed to identify oxidative stress-linked biomarkers and explore their relationship with immune cell infiltration to enhance diagnosis and treatment strategies.
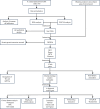
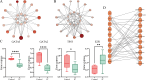
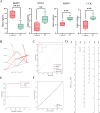
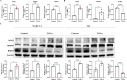
Patients and methods: The GSE711783 dataset from GEO was analyzed to identify differentially expressed genes in ulcerative IC. Oxidative stress-related genes were sourced from GeneCards, with hub genes identified via WGCNA and protein-protein interaction networks. Diagnostic markers were refined using machine learning, and a nomogram prediction model was developed. Diagnostic biomarkers were validated in vitro and in vivo, immune infiltration was assessed with CIBERSORT, and potential therapeutic drugs were identified through DSigDB.
Results: Four diagnostic biomarkers-BMP2, MMP9, CCK, and NOS3-were identified and found to be associated with immune cells, including CD4+ T cells and eosinophils. Decitabine was identified as a potential therapeutic candidate. Experimental validation confirmed the expression of these biomarkers.
Conclusion: This study identifies BMP2, MMP9, CCK, and NOS3 as key biomarkers, offering valuable insights into the diagnosis and treatment of IC.
Keywords: bioinformatics; diagnostic marker; immune landscape; interstitial cystitis; machine learning; oxidative stress.
© 2025 Fu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) report no conflicts of interest in this work. This paper has been uploaded to Research Square as a preprint: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4642942/v1.pdf.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Identification and validation of immune and diagnostic biomarkers for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome by integrating bioinformatics and machine-learning.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 23;16:1511529. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1511529. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39917301 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of PANoptosis-related genes in diabetic retinopathy: machine learning identification and experimental validation.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 4;15:1486251. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1486251. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39697326 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of key biomarkers associated with immune and oxidative stress for preeclampsia by WGCNA and machine learning.Front Genet. 2025 Mar 12;16:1500061. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1500061. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40151199 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of shared biomarkers and drug repurposing in psoriasis and Crohn's disease: integrating bioinformatics, machine learning, and experimental approaches.Front Immunol. 2025 May 8;16:1587705. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587705. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40406126 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of oxidative stress-related diagnostic markers and immune infiltration features for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by bibliometrics and bioinformatics.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 6;11:1356825. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1356825. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39165378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of oxidative stress signature genes in the trabecular meshwork of glaucoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 25;15(1):31260. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16534-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40855175 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

