Prosthetic Rehabilitation of a Post-mucormycosis Maxillectomy Defect Using a Maxillary Hollow Obturator and Complete Denture: A Case Report
- PMID: 40497196
- PMCID: PMC12150251
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.83881
Prosthetic Rehabilitation of a Post-mucormycosis Maxillectomy Defect Using a Maxillary Hollow Obturator and Complete Denture: A Case Report
Abstract
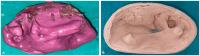
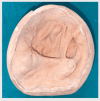
Mucormycosis is an opportunistic fungal infection that severely impacts immunocompromised patients. Invasive mucormycosis tends to require surgical procedures like maxillectomy, leading to a complex oro-nasal communication and a severe compromise of oral function, speech, and esthetics. The following case report describes the prosthetic rehabilitation of a patient after maxillectomy post-mucormycosis. A maxillary complete denture with a closed hollow bulb obturator was constructed to restore oral function, facilitate speech, and improve facial esthetics. The impression-making technique was meticulously altered to obtain a precise recording of the defect, and a new flasking technique was used during processing to create a lightweight yet retentive prosthesis. Thermocol was strategically utilized to hollow the obturator and alveolar ridge segments, thereby reducing the weight while preserving structural support. Soft relining with Molloplast B (Detax GmbH & Co. KG, Ettlingen, Germany) was performed to enhance mucosal adaptation as well as patient comfort. After-insertion assessment indicated optimal fit, retention, and patient satisfaction, with marked improvement in speech and mastication. Follow-up at regular intervals showed maintained function and comfort, underlining the critical role of prosthodontic rehabilitation in the interdisciplinary management of post-mucormycosis maxillary defects.
Keywords: complete denture; maxillofacial prosthesis; mucormycosis; palatal obturator; quality of life.
Copyright © 2025, Srivastava et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures







References
-
- Rhino-orbital mucormycosis in a COVID-19 patient: the first case in Malaysia. Chang CY, Gan YL, Zamri FI, P. Radhakrishnan A. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/20101058221074112 Proc Singapore Healthc. 2022;31:20101058221074112.
-
- Quality of life after maxillectomy and prosthetic obturator rehabilitation. Chigurupati R, Aloor N, Salas R, Schmidt BL. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0278239113001936 J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;1:1471–1478. - PubMed
-
- Surgical and prosthetic reconsiderations in patients with maxillectomy. Lethaus B, Lie N, de Beer F, Kessler P, de Baat C, Verdonck HW. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2842.2009.02031.x. J Oral Rehabil. 2010;37:138–142. - PubMed
-
- A modified technique to fabricate a complete hollow obturator for bilateral maxillectomy in a patient with mucormycosis--a technical case report. Mani UM, Mohamed K, Krishna Kumar A, Inbarajan A. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/scd.12423. Spec Care Dentist. 2019;39:610–616. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
