Characterization of DnaB-DnaG Interaction in M. tuberculosis Using Small-Angle X-ray Scattering-Based Dissociation Assay
- PMID: 40497748
- PMCID: PMC12278352
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202500289
Characterization of DnaB-DnaG Interaction in M. tuberculosis Using Small-Angle X-ray Scattering-Based Dissociation Assay
Abstract
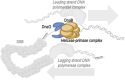
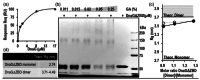
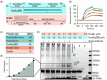
The complex interactions between helicase and primase, two key components of the replisome involved in DNA replication in Mycobacterium tuberculosis are studied. Utilizing purified, complementary domains of these proteins, a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis and a cross-linking assay to characterize their binding dynamics are employed. The SPR analysis reveals a binding dissociation constant of 0.21 ± 0.08 μM, and the cross-linking assay suggests the possible formation of a heterodimer species. Importantly, a small-angle X-ray scattering dissociation assay to study the dynamic interactions between the proteins in solution is utilized. The findings provide new opportunities for targeted therapeutic strategies aimed at DNA replication in M. tuberculosis by revealing the structural interplay between helicase and primase.
Keywords: DnaB; DnaG; protein–protein interactions; small‐angle X‐ray scattering dissociation assay.
© 2025 The Author(s). ChemBioChem published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

