RNF213 Acts as a Molecular Switch for Cav-1 Ubiquitination and Phosphorylation in Human Cells
- PMID: 40497951
- PMCID: PMC12153744
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14110775
RNF213 Acts as a Molecular Switch for Cav-1 Ubiquitination and Phosphorylation in Human Cells
Abstract
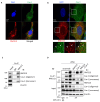
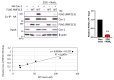
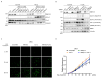
RNF213 encodes a unique protein with AAA+ ATPase and E3 ubiquitin ligase activities that are critical for its diverse roles, which range from involvement in human vasculopathies, such as Moyamoya disease, to ubiquitination of viral and bacterial pathogens. Nevertheless, its primary functions in human signaling remain unclear due to the limited identification of direct substrates. Here, we investigated the interaction between RNF213 and caveolin-1 (Cav-1), a small scaffolding protein vital for caveolae formation and the regulation of a plethora of cellular processes. Cav-1 specifically binds within the two functional AAA+ domains of RNF213 in an ATP-dependent manner, highlighting the influence of cellular energy status on this interaction. Consequently, RNF213 ubiquitinates Cav-1 at several N-terminal lysine residues through K48 and K63 linkages, although several Moyamoya disease-associated RNF213 mutations greatly reduce this polyubiquitination. Moreover, RNF213 activity inhibits phosphorylation of a key regulatory residue of Cav-1, as RNF213 knockdown under oxidative stress markedly enhances Cav-1 Tyr14 phosphorylation and modifies nitric oxide bioavailability in endothelial cells. Collectively, our results indicate that RNF213 functions as a molecular switch modulating Cav-1 signaling based on RNF213 functionality and cellular conditions. These findings offer new insights into vascular pathogenesis and the vast signal pathways along the RNF213-Cav-1 axis.
Keywords: Cav-1; MMD; RNF213; caveolin-1; moyamoya disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Liu W., Morito D., Takashima S., Mineharu Y., Kobayashi H., Hitomi T., Hashikata H., Matsuura N., Yamazaki S., Toyoda A., et al. Identification of RNF213 as a susceptibility gene for moyamoya disease and its possible role in vascular development. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e22542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022542. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

