Extracellular vesicle-mediated mitochondria delivery: Premise and promise
- PMID: 40498574
- PMCID: PMC12158986
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X251349304
Extracellular vesicle-mediated mitochondria delivery: Premise and promise
Abstract
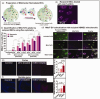
Mitochondrial transfer is highly significant under physiological as well as pathological states given the emerging recognition of mitochondria as cellular "processors" akin to microchip processors that control the operation of a mobile device. Mitochondria play indispensable roles in healthy functioning of the brain, the organ with the highest energy demand in the human body and therefore, loss of mitochondrial function plays a causal role in multiple brain diseases. In this review, we will discuss various aspects of extracellular vesicle (EV)-mediated mitochondrial transfer and their effects in increasing recipient cell/tissue bioenergetics with a focus on these processes in
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles (EVs); medium-to-large EVs; microvesicles; mitochondria; small EVs.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Devika S Manickam is a named inventor on a non-provisional US patent application related to mitochondria-enriched extracellular vesicles.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Delivery of mitochondria via extracellular vesicles - A new horizon in drug delivery.J Control Release. 2022 Mar;343:400-407. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.01.045. Epub 2022 Feb 4. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35131369
-
Mitochondria-containing extracellular vesicles (EV) reduce mouse brain infarct sizes and EV/HSP27 protect ischemic brain endothelial cultures.J Control Release. 2023 Feb;354:368-393. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.01.025. Epub 2023 Jan 18. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 36642252 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-Rich Extracellular Vesicles From Autologous Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Restore Energetics of Ischemic Myocardium.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 Mar 2;77(8):1073-1088. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.12.060. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33632482 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic and diagnostic potential of extracellular vesicle (EV)-mediated intercellular transfer of mitochondria and mitochondrial components.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025 May 14:271678X251338971. doi: 10.1177/0271678X251338971. Online ahead of print. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025. PMID: 40367392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles: opening up a new perspective for the diagnosis and treatment of mitochondrial dysfunction.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Aug 14;22(1):487. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02750-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39143493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Currais A. Ageing and inflammation – a central role for mitochondria in brain health and disease. Age Res Rev 2015; 21: 30–42. - PubMed
-
- Whitaker RM, Corum D, Beeson CC, et al. Mitochondrial biogenesis as a pharmacological target: a new approach to acute and chronic diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2016; 56: 229–249. - PubMed
-
- Moreira PI, Carvalho C, Zhu X, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a trigger of Alzheimer's disease pathophysiology. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1802: 2–10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

