Extraction, purification, in vitro antioxidant and cytoprotective ability of oligostilbenes from paeonia seeds threshing residues
- PMID: 40498758
- PMCID: PMC12156983
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325485
Extraction, purification, in vitro antioxidant and cytoprotective ability of oligostilbenes from paeonia seeds threshing residues
Abstract
Objective: Oligostilbenes, which have been associated with multiple biological activities, are a kind of oligomeric resveratrol compound and widely exist in Paeonia seeds threshing residues. The re-use of the Paeonia seeds threshing residues as value-added materials is, not only cost-effective, but also environmentally beneficial. It is therefore important to develop a high-efficiency method for extraction of oligostilbenes.
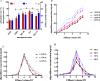
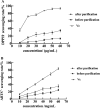
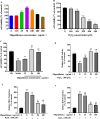
Methods: In this investigation, different extraction methods (soxhlet extraction, high temperature and pressure extraction, cold soaking extraction, heat reflux extraction, and ultrasonic extraction) were used to extract oligostilbenes from Paeonia seeds threshing residues. By comparing the extraction yield and in vitro antioxidant ability of oligostilbenes obtained from different extraction ways, the optimal extraction technology of Paeonia seeds threshing residues oligostilbenes was selected. The macroporous resin was used to purify oligostilbenes crude extract samples, and the purification conditions were determined. The protective effect of purified oligostilbenes on oxidative damage of MODE-K cells was evaluated.
Results: Ultrasonic extraction with ethanol (UA-E) possessed the highest extraction yield of oligostilbenes, and the extraction yield was (3.45 ± 0.07)%. The oligostilbenes extracts obtained by different extraction methods had scavenging ability on DPPH· and ABTS+·, and UA-E showed relatively stronger scavenging ability at different concentration levels. The best resin for purifying oligostilbenes was X-5, and the adsorption and desorption rates were (93.12 ± 0.16)% and (91.33 ± 0.40)%, respectively. The optimal adsorption/desorption conditions were sample loading rate of 2 BV/h, ethanol concentration of 70%, and elution flow rate of 1.0 BV/h. There was a dose-response relationship between the scavenging ability of purified oligostilbenes on DPPH· and ABTS+· and the concentration of the samples. The oligostilbenes could relieve the oxidation effect of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) on MODE-K cells, and enhance the protection of MODE-K cells by regulating the relative SOD activity, MDA, and ROS production.
Conclusion: This research lays a theoretical foundation and scientific reference for the extraction, purification and application of Paeonia seed threshing residues in food and medicine.
Copyright: © 2025 Li et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
NO authors have competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hong DY. Peonies of the world: taxonomy and phytogeography. London, UK: Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2010.
-
- Ekiert H, Klimek-Szczykutowicz M, Szopa A. Paeonia × suffruticosa (Moutan Peony)-A Review of the Chemical Composition, Traditional and Professional Use in Medicine, Position in Cosmetics Industries, and Biotechnological Studies. Plants (Basel). 2022;11(23):3379. doi: 10.3390/plants11233379 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fan Y, Yu L, Zhang L, Chen L, Ning E, Wang X, et al. Preparation, characteristics, and antioxidant activities of carboxymethylated polysaccharides from Paeonia x suffruticosa petals. Process Biochemistry. 2023;133:158–68. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2023.08.001 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

