Caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis converts αSMA+ CAFs into collagen-IIIhigh iCAFs to fuel chemoresistant cancer stem cells
- PMID: 40498841
- PMCID: PMC12154229
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt8697
Caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis converts αSMA+ CAFs into collagen-IIIhigh iCAFs to fuel chemoresistant cancer stem cells
Abstract
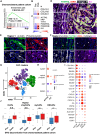
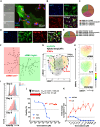
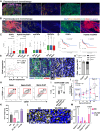
The impact of chemotherapy-induced tumor cell pyroptosis on fibroblasts, a key stromal cell type within the tumor microenvironment (TME), remains unexplored. Here, we report morphologically and molecularly distinct subtypes of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in bladder cancer, including αSMA+IL-6- myofibroblastic CAFs (myCAFs), αSMA-IL-6+ inflammatory CAFs (iCAFs), and hybrid i/myCAFs. Caspase-1-dependent tumor pyroptosis releases several inflammatory chemokines, converting αSMA+ CAF into iCAFs in a CCR6-dependent manner. This is clinically relevant, as a fibroblast gene signature driven by iCAF markers and collagen type III is enriched in patients with chemoresistant bladder cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Contrary to the current notion, iCAFs, rather than myCAFs, produce collagen III in response to chemotherapy, supporting the expansion of cancer stem cells (CSCs). Thus, tumor cell pyroptosis initiates an iCAF-CSC feedforward loop that drives chemoresistance, indicating that inflammatory cell death is not universally beneficial to anticancer therapy, depending on the target cell type.
Figures




References
-
- Lamkanfi M., Dixit V. M., Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell 157, 1013–1022 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Shi J., Zhao Y., Wang K., Shi X., Wang Y., Huang H., Zhuang Y., Cai T., Wang F., Shao F., Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 526, 660–665 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S. A., Abrams J. M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E. S., Altucci L., Amelio I., Andrews D. W., Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M., Antonov A. V., Arama E., Baehrecke E. H., Barlev N. A., Bazan N. G., Bernassola F., Bertrand M. J. M., Bianchi K., Blagosklonny M. V., Blomgren K., Borner C., Boya P., Brenner C., Campanella M., Candi E., Carmona-Gutierrez D., Cecconi F., Chan F. K.-M., Chandel N. S., Cheng E. H., Chipuk J. E., Cidlowski J. A., Ciechanover A., Cohen G. M., Conrad M., Cubillos-Ruiz J. R., Czabotar P. E., D’Angiolella V., Dawson T. M., Dawson V. L., De Laurenzi V., De Maria R., Debatin K.-M., De Berardinis R. J., Deshmukh M., Daniele N. D., Virgilio F. D., Dixit V. M., Dixon S. J., Duckett C. S., Dynlacht B. D., El-Deiry W. S., Elrod J. W., Fimia G. M., Fulda S., García-Sáez A. J., Garg A. D., Garrido C., Gavathiotis E., Golstein P., Gottlieb E., Green D. R., Greene L. A., Gronemeyer H., Gross A., Hajnoczky G., Hardwick J. M., Harris I. S., Hengartner M. O., Hetz C., Ichijo H., Jäättelä M., Joseph B., Jost P. J., Juin P. P., Kaiser W. J., Karin M., Kaufmann T., Kepp O., Kimchi A., Kitsis R. N., Klionsky D. J., Knight R. A., Kumar S., Lee S. W., Lemasters J. J., Levine B., Linkermann A., Lipton S. A., Lockshin R. A., López-Otín C., Lowe S. W., Luedde T., Lugli E., Farlane M. M., Madeo F., Malewicz M., Malorni W., Manic G., Marine J.-C., Martin S. J., Martinou J.-C., Medema J. P., Mehlen P., Meier P., Melino S., Miao E. A., Molkentin J. D., Moll U. M., Muñoz-Pinedo C., Nagata S., Nuñez G., Oberst A., Oren M., Overholtzer M., Pagano M., Panaretakis T., Pasparakis M., Penninger J. M., Pereira D. M., Pervaiz S., Peter M. E., Piacentini M., Pinton P., Prehn J. H. M., Puthalakath H., Rabinovich G. A., Rehm M., Rizzuto R., Rodrigues C. M. P., Rubinsztein D. C., Rudel T., Ryan K. M., Sayan E., Scorrano L., Shao F., Shi Y., Silke J., Simon H.-U., Sistigu A., Stockwell B. R., Strasser A., Szabadkai G., Tait S. W. G., Tang D., Tavernarakis N., Thorburn A., Tsujimoto Y., Turk B., Berghe T. V., Vandenabeele P., Vander Heiden M. G., Villunger A., Virgin H. W., Vousden K. H., Vucic D., Wagner E. F., Walczak H., Wallach D., Wang Y., Wells J. A., Wood W., Yuan J., Zakeri Z., Zhivotovsky B., Zitvogel L., Melino G., Kroemer G., Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 25, 486–541 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Newton K., Strasser A., Kayagaki N., Dixit V. M., Cell death. Cell 187, 235–256 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

