Not all reoperative laparoscopic liver resection procedures are feasible for hepatolithiasis patients with a history of biliary surgery
- PMID: 40501464
- PMCID: PMC12149890
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.105890
Not all reoperative laparoscopic liver resection procedures are feasible for hepatolithiasis patients with a history of biliary surgery
Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic hepatectomy (LH) has been applied in the treatment of hepatolithiasisa in patients with a history of biliary surgery and has already achieved good clinical outcomes. However, reoperative LH (rLH) includes multiple procedures, and the no studies have examined the clinical value of individual laparoscopic procedures.
Aim: To evaluate the safety and feasibility of each rLH procedure for hepatolithiasisa in patients with a history of biliary surgery.
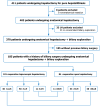
Methods: Patients with previous biliary surgery who underwent reoperative hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis were studied. Liver resection procedures were divided into three categories: (1) Laparoscopic/open left lateral sectionectomy [reoperative laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy (rLLLS)/reoperative open left lateral sectionectomy (rOLLS)]; (2) Laparoscopic/open left hemihepatectomy [reoperative laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy (rLLH)/reoperative open left hemihepatectomy (rOLH)]; and (3) Laparoscopic/open complex hepatectomy [reoperative laparoscopic complex hepatectomy (rLCH)/reoperative open complex hepatectomy (rOCH)]. The clinical outcomes were compared between the rLLLS, rLLH, and rLCH groups, and subgroup analyses were performed for the rLLLS/rOLLS, rLLH/rOLH, and rLCH/rOCH subgroups.
Results: A total of 185 patients were studied, including 101 rLH patients (40 rLLLS, 50 rLLH, and 11 rLCH) and 84 reoperative open hepatectomy (40 rOLLS, 33 rOLH, and 11 rOCH). Among the three types of rLH procedure, rLLLS required the shortest operation time (240.0 minutes vs 325.0 minutes vs 350.0 minutes, P = 0.001) and the lowest blood transfusion rate (10.0% vs 22.0% vs 54.5%, P = 0.005), followed by rLLH. The rLCH had the highest conversion rate (P < 0.05) and postoperative intensive care unit stay rate (P = 0.001). Most clinical outcomes in rLLLS and rLLH were superior or similar to those in the corresponding open surgery, while there were no differences in all outcomes between the rLCH and rOCH subgroups.
Conclusion: The rLH is safe for hepatolithiasis patients with a history of biliary surgery. The rLLLS and rLLH can be recommended for these patients, whereas rLCH should be applied with caution.
Keywords: Conversion; Hepatolithiasis; Laparoscopic hepatectomy; Previous biliary surgery; Reoperation.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- García D, Marino C, Ferreira Coelho F, Rebolledo P, Achurra P, Marques Fonseca G, Kruger JAP, Viñuela E, Briceño E, Carneiro D'Albuquerque L, Jarufe N, Martinez JA, Herman P, Dib MJ. Liver resection for hepatolithiasis: A multicenter experience in Latin America. Surgery. 2023;173:299–304. - PubMed
-
- Yang T, Lau WY, Lai EC, Yang LQ, Zhang J, Yang GS, Lu JH, Wu MC. Hepatectomy for bilateral primary hepatolithiasis: a cohort study. Ann Surg. 2010;251:84–90. - PubMed
-
- Tian J, Li JW, Chen J, Fan YD, Bie P, Wang SG, Zheng SG. The safety and feasibility of reoperation for the treatment of hepatolithiasis by laparoscopic approach. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:1315–1320. - PubMed
-
- Fan Y, Huang J, Xu L, Xu Q, Tang X, Zheng K, Hu W, Liu J, Wang J, Liu T, Liang B, Xiong H, Li W, Fu X, Fang L. Laparoscopic anatomical left hemihepatectomy guided by middle hepatic vein in the treatment of left hepatolithiasis with a history of upper abdominal surgery. Surg Endosc. 2023;37:9116–9124. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

