This is a preprint.
Identification of chromatin-associated RNAs at human centromeres
- PMID: 40501620
- PMCID: PMC12157442
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.05.658139
Identification of chromatin-associated RNAs at human centromeres
Abstract
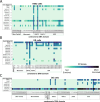
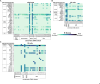
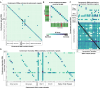
Centromeres are a specialized chromatin domain that are required for the assembly of the mitotic kinetochore and the accurate segregation of chromosomes. Non-coding RNAs play essential roles in regulating genome organization including at the unique chromatin environment present at human centromeres. We performed Chromatin-Associated RNA sequencing (ChAR-seq) in three different human cell lines to identify and map RNAs associated with centromeric chromatin. Centromere enriched RNAs display distinct contact behaviors across repeat arrays and generally belong to three categories: centromere encoded, nucleolar localized, and highly abundant, broad-binding RNAs. Most centromere encoded RNAs remain locally associated with their transcription locus with the exception of a subset of human satellite RNAs. This work provides a comprehensive identification of centromere bound RNAs that may regulate the organization and activity of the centromere.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
