This is a preprint.
Global epistasis in budding yeast driven by many natural variants whose effects scale with fitness
- PMID: 40501638
- PMCID: PMC12154726
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.28.656710
Global epistasis in budding yeast driven by many natural variants whose effects scale with fitness
Update in
-
Global epistasis in budding yeast driven by many natural variants whose effects scale with fitness.Genetics. 2025 Oct 8;231(2):iyaf136. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyaf136. Genetics. 2025. PMID: 40679398 Free PMC article.
Abstract
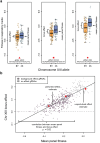
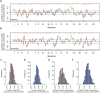
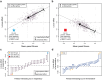
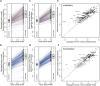
Global epistasis is a phenomenon in which the effects of genetic perturbations depend on the fitness of the individuals in which they occur. In populations with natural genetic variation, global epistasis arises from interactions between perturbations and polymorphic loci that are mediated by fitness. To investigate the prevalence and characteristics of loci involved in these interactions in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we used combinatorial DNA barcode sequencing to measure the fitness of 169 cross progeny (segregants) subjected to 8,126 CRISPRi perturbations across two environments. Global epistasis was evident in these data, with more fit segregants within each environment exhibiting greater sensitivity to genetic perturbations than less fit segregants. We dissected the genetic basis of this global epistasis by scanning the genome for loci whose effects covary with CRISPRi-induced reductions in population fitness. This approach identified 58 loci that interact with fitness, most of which exhibited larger effects in the absence of genetic perturbations. In aggregate, these loci explained the observed global epistasis in each environment and demonstrated that the loci contributing to global epistasis largely overlap with those influencing fitness in unperturbed conditions.
Keywords: background effects; fitness; genetic interactions; genetic perturbations; global epistasis; natural genetic variation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Bachmann M. 2024. rapidfuzz/RapidFuzz: Release 3.8.1. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.10938887. [accessed 2025 Jan 25]. https://zenodo.org/records/10938887. - DOI
-
- Barter R, Yu B. 2017. superheat: A Graphical Tool for Exploring Complex Datasets Using Heatmaps. [accessed 2025 Jan 25]. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/superheat/index.html.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
