This is a preprint.
Analysis of isobaric quantitative proteomic data using TMT-Integrator and FragPipe computational platform
- PMID: 40501722
- PMCID: PMC12154698
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.27.656447
Analysis of isobaric quantitative proteomic data using TMT-Integrator and FragPipe computational platform
Abstract
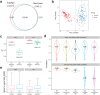
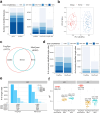
Isobaric mass tags, such as iTRAQ and TMT, are widely utilized for peptide and protein quantification in multiplex quantitative proteomics. We present TMT-Integrator, a bioinformatics tool for processing quantitation results from TMT and iTRAQ experiments, offering integrative reports at the gene, protein, peptide, and post-translational modification site levels. We demonstrate the versatility of TMT-Integrator using five publicly available TMT datasets: an E. coli dataset with 13 spike-in proteins, the clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) whole proteome and phosphopeptide-enriched datasets from the Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium, and two human cell lysate datasets showcasing the latest advances with the Astral instrument and TMT 35-plex reagents. Integrated into the widely used FragPipe computational platform (https://fragpipe.nesvilab.org/), TMT-Integrator is a core component of TMT and iTRAQ data analysis workflows. We evaluate the FragPipe/TMT-Integrator analysis pipeline's performance against MaxQuant and Proteome Discoverer with multiple benchmarks, facilitated by the bioinformatics tool OmicsEV. Our results show that FragPipe/TMT-Integrator quantifies more proteins in the E. coli and ccRCC whole proteome datasets, identifies more phosphorylated sites in the ccRCC phosphoproteome dataset, and delivers overall more robust quantification performance compared to other tools.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST A.I.N. is the Founder of Fragmatics and serves on the scientific advisory boards of Protai Bio, Infinitopes, and Mobilion Systems. A.I.N. is also a paid consultant for Novartis. A.I.N. and F.Y. have a financial interest due to the licensing of MSFragger and IonQuant to commercial entities. Other authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Aebersold R. and Mann M., Mass-spectrometric exploration of proteome structure and function. Nature, 2016. 537(7620): p. 347–355. - PubMed
-
- Ross P.L., et al. , Multiplexed Protein Quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Using Amine-reactive Isobaric Tagging Reagents. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2004. 3(12): p. 1154–1169. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
