This is a preprint.
Structural insights into VRC01-class bnAb precursors with diverse light chains elicited in the IAVI G001 human vaccine trial
- PMID: 40501797
- PMCID: PMC12154976
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.22.655646
Structural insights into VRC01-class bnAb precursors with diverse light chains elicited in the IAVI G001 human vaccine trial
Abstract
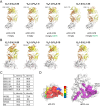
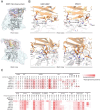
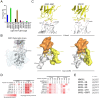
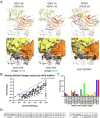
The development of germline-targeting vaccines represents a potentially transformative strategy to elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) against HIV and other antigenically diverse pathogens. Here, we report on structural characterization of vaccine-elicited VRC01-class bnAb precursors in the IAVI G001 Phase 1 clinical trial with the eOD-GT8 60mer nanoparticle as immunogen. High-resolution X-ray structures of eOD-GT8 monomer complexed with Fabs of five VRC01-class bnAb precursors with >90% germline identity revealed a conserved mode of binding to the HIV CD4-binding site (CD4bs) via IGHV1-2-encoded heavy chains, mirroring mature bnAb interactions. The light-chain V-gene diversity emulated VRC01 bnAbs and stabilized antigen engagement, while their conserved five-residue LCDR3 motifs prevented steric clashes. Notably, the VRC01-class bnAb precursors accommodated the N276 glycan, a key barrier in HIV Env recognition, through structural rearrangements in HCDR3 or LCDR1, despite its absence in the immunogen. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) analysis showed that 87% of elicited antibodies retained glycan binding capacity, albeit with reduced affinity. These findings validate the ability of eOD-GT8 60mer nanoparticles to prime VRC01-class bnAb precursors with native-like paratopes but with intrinsic glycan adaptability. Structural mimicry of mature bnAbs was observed even with limited somatic hypermutation, indicating that critical features are encoded in the germline repertoire. The structures highlight how germline-encoded features drive bnAb-like recognition at early stages. This work provides molecular evidence supporting germline-targeting in humans and provides guidance for designing booster immunogens to shepherd affinity maturation toward broad neutralization.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest Statement W.R.S. is an inventor on patents filed by Scripps and IAVI on the eOD-GT8 monomer and 60mer immunogens. W.R.S. is an employee and shareholder of Moderna, Inc. The other authors have no competing interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural insights into VRC01-class bnAb precursors with diverse light chains elicited in the IAVI G001 human vaccine trial.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Aug 19;122(33):e2510163122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2510163122. Epub 2025 Aug 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40789024 Clinical Trial.
-
Dual Role of Glycosylation in Resistance to CD4-binding Site Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 18:2025.07.15.664896. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.15.664896. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40791402 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Heterologous prime-boost vaccination drives early maturation of HIV broadly neutralizing antibody precursors in humanized mice.Sci Transl Med. 2024 May 22;16(748):eadn0223. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adn0223. Epub 2024 May 22. Sci Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38753806 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery medicine - the HVTN's iterative approach to developing an HIV-1 broadly neutralizing vaccine.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2023 Nov 1;18(6):290-299. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000821. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2023. PMID: 37712873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
