This is a preprint.
Prenatal alcohol exposure promotes nerve injury-induced pathological pain following morphine treatment via NLRP3-mediated peripheral and central proinflammatory immune actions
- PMID: 40501832
- PMCID: PMC12154580
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.30.655639
Prenatal alcohol exposure promotes nerve injury-induced pathological pain following morphine treatment via NLRP3-mediated peripheral and central proinflammatory immune actions
Update in
-
Prenatal alcohol exposure promotes nerve injury-induced pathological pain following morphine treatment via NLRP3-mediated peripheral and central proinflammatory immune actions.Brain Behav Immun. 2025 Oct;129:736-756. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2025.06.041. Epub 2025 Jul 6. Brain Behav Immun. 2025. PMID: 40628342
Abstract
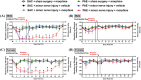
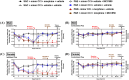
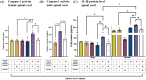
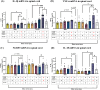
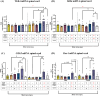
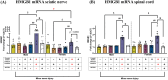
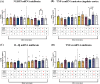
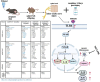
Adverse in-utero conditions may exert a lifelong impact on neuroimmune function. Our prior work showed that prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) increases pathological pain sensitivity (allodynia) following peripheral sciatic nerve injury. While the immune mechanism(s) of PAE-induced immune dysfunction are poorly understood, prior studies implicated the involvement of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and the nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat-containing family, pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasomes. Interestingly, emerging data suggest a surprising overlap of spinal glial proinflammatory activation via the TLR4-NLRP3-interleukin (IL)-1β axis due to opioid treatment in nerve-injured non-PAE rodents. Considering this preclinical evidence, we explored whether PAE poses a risk factor in creating proinflammatory immune bias consequent to opioid (morphine) exposure. We hypothesized that under nerve injury conditions, PAE may interact with morphine, promoting peripheral and CNS proinflammatory factors in a NLRP3-dependent manner. Using a minor nerve injury model in adult mice, we demonstrate that PAE prolongs the chronicity of ongoing allodynia in both sexes, with a more pronounced effect observed in male mice. Our study shows that PAE amplifies proinflammatory responses at the injury site and the spinal cord, driving morphine-prolonged allodynia through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Furthermore, high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), a well-established pain-promoting TLR4 agonist, is elevated in allodynic PAE mice. NLRP3 inhibitor, MCC950, effectively reverses morphine-induced allodynia and reduces Caspase-1 activity, IL-1β, and related proinflammatory factors. Although few sex-specific effects were observed, our data convincingly support that PAE and morphine interactions ultimately converge on NLRP3-driven mechanisms in both sexes. Together, this study suggests that PAE modulates later-life neuroimmune function and provides critical insights into immune regulators underlying PAE-induced biological vulnerability to pathological pain processing and adverse effects of opioids.
Keywords: MCC950; NLRP3 inflammasome; Prenatal alcohol exposure; allodynia; cytokines; glia; interleukin −1β; morphine; neuroimmune; peripheral immune.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this study.
Figures


References
-
- B F. & L X. Sensory Processing in Young Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. Physical & Occupational Therapy In Pediatrics 39, (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
