This is a preprint.
Germline polymorphisms in the immunoglobulin kappa and lambda loci explain variation in the expressed light chain antibody repertoire
- PMID: 40501977
- PMCID: PMC12154815
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.28.656470
Germline polymorphisms in the immunoglobulin kappa and lambda loci explain variation in the expressed light chain antibody repertoire
Update in
-
Germline polymorphisms in the immunoglobulin kappa and lambda loci underpinning antibody light chain repertoire variability.Nat Commun. 2025 Nov 28;16(1):11707. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-66759-9. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 41315391 Free PMC article.
Abstract
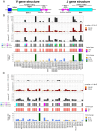
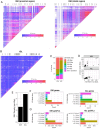
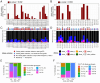
Variation in antibody (Ab) responses contributes to variable disease outcomes and therapeutic responsiveness, the determinants of which are incompletely understood. This study demonstrates that polymorphisms in immunoglobulin (IG) light chain loci dictate the composition of the Ab repertoire, establishing fundamental baseline differences that preclude functional Ab-mediated responses. Using long-read genomic sequencing of the IG kappa (IGK) and IG lambda (IGL) loci, we comprehensively resolved genetic variation, including novel structural variants, single nucleotide variants, and gene alleles. By integrating these genetic data with Ab repertoire profiling, we found that all forms of IG germline variation contributed to inter-individual gene usage differences for >70% of light chain genes in the repertoire, directly impacting the amino acids of expressed light chain transcripts, including complementarity determining region domains. The genomic locations of usage - associated variants in both intergenic and coding regions indicated that IG polymorphisms modulate gene usage via diverse mechanisms, likely including the modulation of V(D)J recombination, heavy and light chain pairing biases, and transcription/translation. Finally, relative to IGL, IGK was characterized by more extensive linkage disequilibrium and genetic co-regulation of gene usage, illuminating differential regulatory and evolutionary features between the two light chain loci. These results firmly establish the critical contribution of IG light chain polymorphism in Ab repertoire diversity, with important implications for investigating Ab responses in health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests C.T.W., M.L.S., and W.L. are founders and shareholders of Clareo Biosciences, Inc. and serve on its Executive Board.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
