This is a preprint.
Analysis of Essential Genes in Clostridioides difficile by CRISPRi and Tn-seq
- PMID: 40502013
- PMCID: PMC12157513
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.04.657922
Analysis of Essential Genes in Clostridioides difficile by CRISPRi and Tn-seq
Abstract
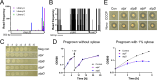
Essential genes are interesting in their own right and as potential antibiotic targets. To date, only one report has identified essential genes on a genome-wide scale in Clostridioides difficile, a problematic pathogen for which treatment options are limited. That foundational study used large-scale transposon mutagenesis to identify 404 protein-encoding genes as likely to be essential for vegetative growth of the epidemic strain R20291. Here, we revisit the essential genes of strain R20291 using a combination of CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) and transposon-sequencing (Tn-seq). First, we targeted 181 of the 404 putatively essential genes with CRISPRi. We confirmed essentiality for >90% of the targeted genes and observed morphological defects for >80% of them. Second, we conducted a new Tn-seq analysis, which identified 346 genes as essential, of which 283 are in common with the previous report and might be considered a provisional essential gene set that minimizes false positives. We compare the list of essential genes to those of other bacteria, especially Bacillus subtilis, highlighting some noteworthy differences. Finally, we used fusions to red fluorescent protein (RFP) to identify 18 putative new cell division proteins, three of which are conserved in Bacillota but of largely unknown function. Collectively, our findings provide new tools and insights that advance our understanding of C. difficile.
Keywords: CRISPRi; Tn-seq.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular feature-based classification of retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a prospective cohort study.Elife. 2025 May 23;14:RP100887. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100887. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40407808 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction, screening and characterization of novel bioactive tetrapeptide matrikines for skin rejuvenation.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):92-106. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae061. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38375775
-
Use of β-adrenoreceptor drugs and Parkinson's disease incidence in women from the French E3N cohort study.J Parkinsons Dis. 2025 Jun;15(4):789-804. doi: 10.1177/1877718X251330993. Epub 2025 Apr 29. J Parkinsons Dis. 2025. PMID: 40302366
-
Defining disease severity in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis for the application to biomarker research: an interdisciplinary perspective.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):14-23. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae080. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38419411 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- CDC. 2019. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
