This is a preprint.
A Transcriptomics-Based Computational Drug Repositioning Pipeline Identifies Simvastatin And Primaquine As Novel Therapeutics For Endometriosis Pain
- PMID: 40502156
- PMCID: PMC12154721
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.05.28.656743
A Transcriptomics-Based Computational Drug Repositioning Pipeline Identifies Simvastatin And Primaquine As Novel Therapeutics For Endometriosis Pain
Abstract
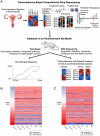
Introduction and methods: Endometriosis has limited treatment options, prompting the search for novel therapeutics. We previously used a transcriptomics-based computational drug repositioning pipeline to analyze public bulk transcriptomic data and identified several drug candidates. Fenoprofen, our top in silico candidate, was validated in a rat model. Building on this, we now evaluate two additional candidates, simvastatin (a cholesterol-lowering drug) and primaquine (an antimalarial), based on strong gene expression reversal scores and favorable safety profiles. Using a validated rat model of endometriosis and pain, we conducted behavioral testing, bulk RNA sequencing, and differential expression analysis to assess their therapeutic potential.
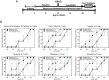
Results: Of 299 drugs identified computationally, simvastatin and primaquine ranked highly for reversing gene expression signatures associated with endometriosis. In vivo validation using a rat model of endometriosis demonstrated that both drugs significantly reduced vaginal hyperalgesia, a surrogate marker of endometriosis-associated pain. RNA-seq of uteri and lesions confirmed reversal of disease-associated gene expression signatures following treatment.
Conclusion: Simvastatin and primaquine attenuated pain behaviors and reversed endometriosis-related gene expression changes in an animal model. These findings highlight their potential as repurposed therapeutics for endometriosis-related pain and support the effectiveness of computational drug repositioning strategies in identifying new treatment strategies.
Keywords: bioinformatics; drug repositioning; endometriosis; therapeutics; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-Interest Statement: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
