Toward Automated Clinical Transcriptions
- PMID: 40502215
- PMCID: PMC12150720
Toward Automated Clinical Transcriptions
Abstract
Administrative documentation is a major driver of rising healthcare costs and is linked to adverse outcomes, including physician burnout and diminished quality of care. This paper introduces a secure system that applies recent advancements in speech-to-text transcription and speaker-labeling (diarization) to patient-provider conversations. This system is optimized to produce accurate transcriptions and highlight potential errors to promote rapid human verification, further reducing the necessary manual effort. Applied to over 40 hours of simulated conversations, this system offers a promising foundation for automating clinical transcriptions.
©2025 AMIA - All rights reserved.
Figures
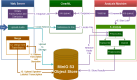
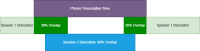



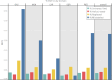
References
-
- Bredin H. pyannote-audio [Internet] GitHub. 2023 [cited 2024 Sep 16] Available from: https://github.com/pyannote/pyannote-audio .
-
- Radford A, Kim J. W, Xu T, Brockman G, McLeavey C, Sutskever I. Robust speech recognition via large-scale weak supervision [Internet] arXiv. 2022 [cited 2024 Sep 16] Available from: https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.04356 .
-
- MinIO documentation MinIO for kubernetes [Internet] 2023 [cited 2024 Sep 16] Available from: https://min.io/docs/minio/kubernetes/upstream/
-
- ClearML documentation [Internet] 2023 [cited 2024 Sep 16] Available from: https://clear.ml/docs/latest/docs/
-
- Bredin H. Pyannote speaker-diarization-3.1 [Internet] 2024 [cited 2024 Sep 16] Available from: https://huggingface.co/pyannote/speaker-diarization-3.1 .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
