Functionality of garlic sulfur compounds (Review)
- PMID: 40502354
- PMCID: PMC12150274
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2025.2002
Functionality of garlic sulfur compounds (Review)
Abstract
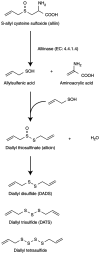
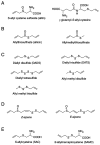
Garlic (Allium sativum L.), a perennial herbaceous edible plant, is classified in the Amaryllidaceae family and belongs to the Allium genus. It has a higher sulfur content than other plants. Garlic is extensively used worldwide as a spice and flavoring agent, and it generates a unique aroma during cooking. Garlic possesses various properties, including anti-thrombotic, antioxidant, blood cholesterol-lowering, anti-obesity and anti-dementia effects. These properties have been attributed to various garlic-derived sulfur-containing compounds, including S-allyl cysteine, allicin, allyl sulfides and ajoene. The present review provides an overview of the mechanisms that underlie the generation of odor compounds in garlic and discusses certain observed effects of garlic consumption.
Keywords: AGE; DATS; allicin; alliin; garlic; organosulfur compound.
Copyright: © 2025 Seki and Hosono.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial support for this publication was received from Wakunaga Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Figures
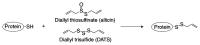
References
-
- Seki T, Hosono T, Ozaki-Masuzawa Y. Chemistry of sulfur-containing compounds derived from garlic and their functions-from the history of garlic to its physiological functions concerning lifestyle-related disease. In: Chemistry of Korean Foods and Beverages (ACS Symposium Series Vol. 1303). Do CH, Rimando AM and Kim Y (eds). American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp43-55, 2019.
-
- Yamazaki M, Sugiyama M, Saito K. Intercellular localization of cysteine synthase and alliinase in bundle sheaths of allium plants. Plant Biotechnol. 2002;19:7–10.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
