Combined TNF-α and OX40L targeting as a new treatment option for hidradenitis suppurativa
- PMID: 40502542
- PMCID: PMC12155757
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacig.2025.100483
Combined TNF-α and OX40L targeting as a new treatment option for hidradenitis suppurativa
Abstract
Background: Chronic inflammatory conditions are among the leading causes of disability and mortality. Although therapies have been significantly improved with the introduction of target-specific biologics, many chronic inflammatory conditions can be only moderately controlled by inhibition of individual cytokines.
Objective: We sought to compare individual versus simultaneous blockade of TNF-α and OX40L in controlling inflammation.
Methods: Analysis was conducted of the murine xenograft graft-versus-host disease model, a novel cynomolgus monkey model of simultaneous T cell-dependent antibody response (TDAR) and delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) skin reaction, and samples of patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
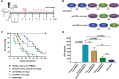
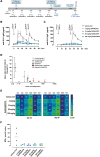
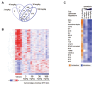
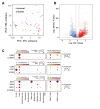
Results: Compared with individual inhibition, combined targeting of TNF-α and OX40L using mAbs more potently suppressed TDAR and DTH in cynomolgus monkey. We therefore created SAR442970, a bispecific pentavalent Nanobody containing 2 domains each binding to OX40L and TNF-α and 1 domain binding serum albumin to extend half-life. In xenograft graft-versus-host disease, disease control by SAR442970 was superior compared with treatment with monospecific anti-TNF-α or anti-OX40L Nanobodies. In cynomolgus monkey, SAR442970 potently suppressed TDAR and DTH. The transcriptional signature of inflamed monkey skin showed similarities to that of lesional skin of patients with atopic dermatitis and, even more so, HS and was inhibited by SAR442970 treatment. Increased numbers of cells expressing OX40 were observed in HS lesions, and bioinformatics analyses of single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing data identified cells expressing OX40 as T cells with a highly mobile phenotype.
Conclusion: OX40-OX40L interaction is a key pathogenetic feature in HS, and patients with HS might benefit from combined TNF-α/OX40L blockade by SAR442970, which is currently investigated in a clinical phase 2 trial.
Keywords: Nanobody; OX40; OX40L; T cell–dependent antibody response; TNF-α; delayed-type hypersensitivity skin reaction; hidradenitis suppurativa; xenograft graft-versus-host disease.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The study was entirely funded by 10.13039/100004339Sanofi. Disclosure of potential conflict of interest: T. Leeuw, D. Šimaitė, K. Heyninck, C. Levin, H. Rommelaere, Y. Hijazi, T. Kreutzberg, S. Cornelis, M. Kohlmann, F. Nestle, and M. Herrmann are Sanofi employees, and some are shareholders. Data are included in pending patents on which T. Leeuw, K. Heyninck, S. Cornelis, H. Rommelaere, T. Kreutzberg, and P. Florian are coinventors (international patent application no. PCT/EP2020/084431; title: “Polypeptides comprising immunoglobulin single variable domains targeting tnfa and ox40l”). R. Sabat and K. Wolk have received research grants, scientific awards, or honoraria for participation in advisory boards, clinical trials, or as speaker for one or more of the following: AbbVie, Amgen, Bayer, 10.13039/100006314Biogen Idec, 10.13039/100008349Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, 10.13039/100006436Celgene, Charité Research Organisation, 10.13039/100008322CSL Behring, Dr Willmar Schwabe, Flexopharm, 10.13039/100015756Janssen-Cilag, La Roche-Posay Laboratoire Dermatologique, 10.13039/100008792Novartis Pharma, Parexel, Pfizer, Sanofi, TFS Trial Form Support, and UCB Pharma. T.-C. Brembach declares that she has no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Conrad N., Misra S., Verbakel J.Y., Verbeke G., Molenberghs G., Taylor P.N., et al. Incidence, prevalence, and co-occurrence of autoimmune disorders over time and by age, sex, and socioeconomic status: a population-based cohort study of 22 million individuals in the UK. Lancet. 2023;401:1878–1890. - PubMed
-
- Marshall D.C., Al Omari O., Goodall R., Shalhoub J., Adcock I.M., Chung K.F., et al. Trends in prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life-years relating to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Europe: an observational study of the global burden of disease database, 2001-2019. BMC Pulm Med. 2022;22:289. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ghoreschi K., Balato A., Enerbäck C., Sabat R. Therapeutics targeting the IL-23 and IL-17 pathway in psoriasis. Lancet. 2021;397:754–766. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

