Signal-domain speed-of-sound correction for ring-array-based photoacoustic tomography
- PMID: 40502803
- PMCID: PMC12156271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pacs.2025.100735
Signal-domain speed-of-sound correction for ring-array-based photoacoustic tomography
Abstract
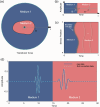
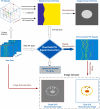
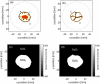
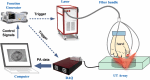
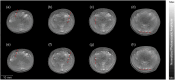
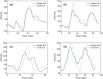
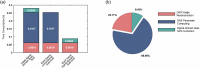
Photoacoustic imaging combines the advantages of optical and acoustic imaging, making it a promising tool in biomedical imaging. Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) reconstructs images by solving the inverse problem from detected photoacoustic waves to initial pressure map. The heterogeneous speed of sound (SoS) distribution in biological tissue significantly affects image quality, as uncertain SoS variations can cause image distortions. Previously reported dual-speed-of-sound (dual-SoS) imaging methods effectively address these distortions by accounting for the SoS differences between tissues and the coupling medium. However, these methods require recalculating the distribution parameters of the SoS for each frame during dynamic imaging, which is highly time-consuming and poses a significant challenge for achieving real-time dynamic dual-SoS PAT imaging. To address this issue, we propose a signal-domain dual-SoS correction method for PAT image reconstruction. In this method, two distinct SoS regions are differentiated by recognizing the photoacoustic signal features of the imaging target's contours. The signals are then corrected based on the respective SoS values, enabling signal-domain-based dual-SoS dynamic real-time PAT imaging. The proposed method was validated through numerical simulations and in-vivo experiments of human finger. The results show that, compared to the single-SoS reconstruction method, the proposed approach produces higher-quality images, achieving the resolution error by near 12 times and a 30 % increase in contrast. Furthermore, the method enables dual-SoS dynamic real-time PAT reconstruction at 10 fps, which is 187.22 % faster than existing dual-SoS reconstruction methods, highlighting its feasibility for dynamic PAT imaging of heterogeneous tissues.
Keywords: Image reconstruction; Photoacoustic tomography; Speed correction; Speed of sound.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

