Heterologous prime-boost vaccination drives stromal activation and adaptive immunity against SARS-CoV-2 variants
- PMID: 40503231
- PMCID: PMC12151836
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1597417
Heterologous prime-boost vaccination drives stromal activation and adaptive immunity against SARS-CoV-2 variants
Abstract
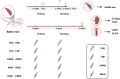
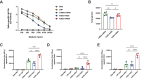
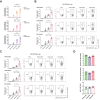
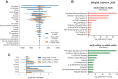
Heterologous vaccination strategies have shown superior efficacy over homologous regimens in clinical studies, but the underlying immunological mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Using a mouse model, we investigated the immune responses induced by heterologous prime-boost vaccination with adenoviral and mRNA vaccines. Heterologous vaccination (adenoviral prime, mRNA boost) elicited higher neutralizing antibody titers and stronger CD8+ T cell responses against Delta and Omicron-BA.5 variants compared to homologous regimens. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of injection-site tissues revealed that adenoviral priming induced minimal changes in cellular composition but established a pre-conditioned innate immune environment. This effect was further amplified upon mRNA boosting, particularly through fibroblast-driven chemokine responses that promoted immune cell recruitment. These findings suggest that adenoviral priming enhances local immune activation upon boosting, contributing to the heightened adaptive immune response observed in heterologous vaccination. This study provides mechanistic insights into the immunological effects of heterologous prime-boost strategies against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Keywords: COVID-19; adenoviral vaccine; cross immunity; heterologous vaccination; immune response; mRNA vaccine; single cell transcriptional analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Jeon, Kim, Kim, Shin, Park, Chang, Kang, Kim, Park, Youk, Kim and Yeo.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors K-SS, BP, SC, and C-YK were employed by the company Cellid Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Costa Clemens SA, Weckx L, Clemens R, Almeida Mendes AV, Ramos Souza A, Silveira MBV, et al. Heterologous versus homologous COVID-19 booster vaccination in previous recipients of two doses of CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccine in Brazil (RHH-001): a phase 4, non-inferiority, single blind, randomised study. Lancet. (2022) 399:521–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00094-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

