Treatment strategies targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mechanistic target of rapamycin pathway against triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 40503407
- PMCID: PMC12149821
- DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.104623
Treatment strategies targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mechanistic target of rapamycin pathway against triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
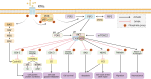
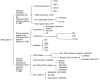
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an exceptionally aggressive subtype of breast cancer with a poor prognosis. TNBC patients have limited treatment options beyond conventional chemotherapy, and they face significant challenges associated with disease recurrence and resistance to chemotherapy. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in cell proliferation, growth, metabolism, and survival. Its aberrant activation is closely linked to the development and progression of TNBC, as well as treatment response and drug resistance. Currently, numerous targeted drugs specifically inhibiting this signaling pathway are being developed and undergoing clinical trials. These include inhibitors targeting PI3K, AKT, or mTOR individually, as well as dual-target or multi-target inhibitors simultaneously targeting different components of this pathway. Encouragingly, some inhibitors have demonstrated promising potential in clinical trials. This review delves into the therapeutic potential of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway for TNBC and explores prospects for drug discovery.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Inhibitors; Mechanistic target of rapamycin; Natural products; Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Protein kinase B; Therapy; Triple negative breast cancer.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Polk A, Svane IM, Andersson M, Nielsen D. Checkpoint inhibitors in breast cancer - Current status. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;63:122–134. - PubMed
-
- Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Newman LA, Freedman RA, Smith RA, Star J, Jemal A, Siegel RL. Breast cancer statistics 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:477–495. - PubMed
-
- da Silva JL, Cardoso Nunes NC, Izetti P, de Mesquita GG, de Melo AC. Triple negative breast cancer: A thorough review of biomarkers. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020;145:102855. - PubMed
-
- Jiang YZ, Ma D, Suo C, Shi J, Xue M, Hu X, Xiao Y, Yu KD, Liu YR, Yu Y, Zheng Y, Li X, Zhang C, Hu P, Zhang J, Hua Q, Zhang J, Hou W, Ren L, Bao D, Li B, Yang J, Yao L, Zuo WJ, Zhao S, Gong Y, Ren YX, Zhao YX, Yang YS, Niu Z, Cao ZG, Stover DG, Verschraegen C, Kaklamani V, Daemen A, Benson JR, Takabe K, Bai F, Li DQ, Wang P, Shi L, Huang W, Shao ZM. Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers: Subtypes and Treatment Strategies. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:428–440.e5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

