Nigeria's public health response to disease outbreaks: A review of strengths and weaknesses
- PMID: 40503462
- PMCID: PMC12152679
- DOI: 10.4102/jphia.v15i1.773
Nigeria's public health response to disease outbreaks: A review of strengths and weaknesses
Abstract
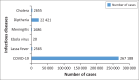
Background: In the past 20 years, Nigeria has confronted an array of six significant infectious disease outbreaks, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Lassa fever, meningitis, diphtheria, cholera and Ebola. Although the country has generally managed to address most of these infections effectively, there are still some shortcomings in the nation's public health response.
Aim: This review examined the six most significant outbreaks of infectious diseases and the corresponding public health responses, evaluating the strengths and limitations of the country's public health system.
Setting: This study focused on Nigeria. Nigeria is regarded as a country with the largest population in Africa.
Method: A narrative review approach was employed, which entailed identifying pertinent literature using search terms with various Boolean combinations derived from multiple electronic databases, including PubMed, Google Scholar, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) database, the Web of Science and Africa Journals Online.
Results: The key strengths of Nigeria's public health system include surveillance, workforce development, prevention at entry points, risk communication and establishment of national reference libraries. However, the study also identified several areas of weakness, such as inadequate funding, inadequate efforts at the subnational level, poor coordination between public health and security authorities, a lack of integration between the animal and human health sectors, inadequate biosafety and biosecurity policies and programmes and logistical complexities.
Conclusion: Despite the strengths, there are still weaknesses within Nigeria's public health system response to infectious diseases.
Contribution: The study outlined the various strengths and weaknesses of the Nigeria Public health system in combating infectious disease. Therefore, it is recommended that funding be increased, poverty and inequalities are addressed, efforts at the subnational level be increased, and a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between the public health sector and security authorities be established.
Keywords: Nigeria; infectious disease; outbreak; public health; response; strategy.
© 2024. The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationships that may have inappropriately influenced them in writing this article.
Figures
References
-
- Statista . Population in Africa 2023, by country [homepage on the Internet]. Statista; 2024. [cited 2024 Jan 15]. Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1121246/population-in-africa-by-coun...
-
- Fengler W. Can rapid population growth be good for economic development? [homepage on the Internet]. World Bank Blogs; 2024. [cited 2024 Jan 15]. Available from: https://blogs.worldbank.org/en/africacan/can-rapid-population-growth-be-...
-
- Idajili A, Adebayo TA, Chijioke UW, Irowa-Omoregie D. The impact of global infectious diseases on Nigeria’s socioeconomic development. Afr J Soc Sci Hum Res [serial online]. 2020. [cited 2024 Jan 16];3(6):232–245. Available from: https://abjournals.org/ajsshr/wp-content/uploads/sites/9/journal/publish...
-
- Tropical medicine and infectious disease [homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 15]. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/tropicalmed/special_issues/poverty
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous