Emerging Capabilities of Nonclassical Noncovalent Interactions and Asymmetric Catalysis in Stereoselective Glycosylations and Carbohydrate Functionalizations
- PMID: 40503847
- PMCID: PMC12224338
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5c00289
Emerging Capabilities of Nonclassical Noncovalent Interactions and Asymmetric Catalysis in Stereoselective Glycosylations and Carbohydrate Functionalizations
Abstract
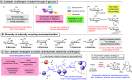
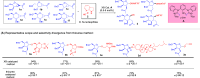
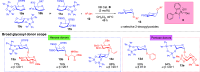
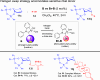
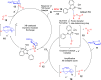
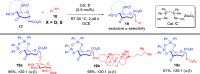
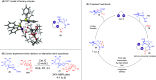
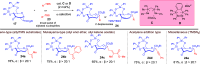
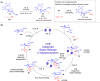
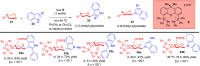
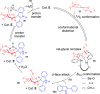
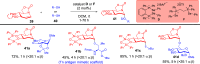
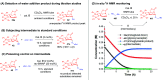
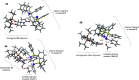
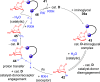
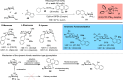
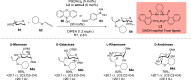
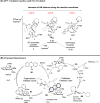
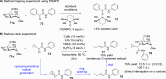
ConspectusDeriving inspiration from frontier catalytic paradigms has emerged as a major force to tackle long-standing stereoselectivity issues in carbohydrate synthesis. In particular, there is a strong momentum in the harnessing of nonclassical σ-hole based noncovalent interactions (NCIs) in chemical glycosylations and the use of asymmetric catalysis to surmount the formidable site-selectivity challenge in the functionalization of carbohydrate polyols.In this Account, we describe our pioneering contributions to advancing these two major directions. First, we introduce our early work whereby halogen bonding (XB) interactions could be harnessed catalytically on sugars. We realized that the polyoxygenated motifs embedded in different regions of the carbohydrate scaffold offered multiple anchoring points where the XB-catalyst could iteratively interact via halogen···O interactions. As a consequence, a counterintuitive multistage XB-activation concept was discovered. In our XB-catalyzed strain-release glycosylation, we intriguingly observed substantial elevation of anomeric selectivity over a wide array of glycosyl substrates as compared with thiourea catalysis. In XB-catalyzed 2-deoxyglycosylations, the multistaged XB-activation phenomena was also operative. Apart from the broader tolerance of glycosyl donors/acceptors compared to thiourea catalysis, we demonstrated the halogen tunability concept, where a halogen swap on the catalyst enabled tolerance of sensitive pentose-based donors.Next, we discovered that the two σ-holes per chalcogen property of phosphonochalcogenide (PCH) catalysts imparted unique benefits in glycoside activation. This opened up an unknown bifurcated chalcogen bonding (ChB) activation concept that paved a stereoselective entry into 7-ring sugars through either an internal nucleophilic substitution (SNi) type mechanism or an intramolecular aglycone transposition strategy. C- and N-glycosylations of indoles with glycals were realized through conformational distortion by a network of ChB and π-interactions. The exclusively α-selective O- and S-iminoglycosylation of iminoglycals was further developed through an unprecedented multistep ChB-activation manifold.Second, our investigations revealed that multiple stereoselectivity challenges in site-selective carbohydrate functionalizations can be concomitantly tackled by an asymmetric catalytic system. Departing from the classical use of asymmetric catalysis to create chiral centers on achiral substrates, we advanced stereochemical complexity generation on sugars by simultaneously addressing the site-, diastereo-, and enantioselectivity challenges when carbohydrate polyols react with prochiral electrophiles. Additionally, rarely observed dynamic kinetic resolution type glycosylations on reducing sugars were unravelled when chiral Rh(I) and chiral copper catalytic systems were employed. We also discovered that the multiple stereoselectivity control by chiral Pd/organoboron-catalyzed site-selective functionalization of carbohydrate polyols can be attributed to the vital stereocontrolling role of NCIs such as CH-π interactions and hydrogen bonding.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Role of Anions in Guanidinium-Catalyzed Chiral Cation Ion Pair Catalysis.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Jul 15;58(14):2269-2281. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5c00283. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 40587427
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Oxidation of Disparate Functional Groups Mediated by a Common Aspartic Acid-Based Peptide Catalyst Platform.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Jul 1;58(13):2072-2087. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5c00247. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 40530828
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions targeted at women to encourage the uptake of cervical screening.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 6;9(9):CD002834. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002834.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34694000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rao V. U. B., Wang C., Demarque D. P., Grassin C., Otte F., Merten C., Strohmann C., Loh C. C. J.. A synergistic Rh(I)/organoboron-catalysed site-selective carbohydrate functionalization that involves multiple stereocontrol. Nat. Chem. 2023;15:424–435. doi: 10.1038/s41557-022-01110-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

