Intramyocardial injection of pre-cultured endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells inside alginate/gelatin microspheres induced angiogenesis in infarcted rabbits
- PMID: 40506721
- PMCID: PMC12164120
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-025-02301-0
Intramyocardial injection of pre-cultured endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells inside alginate/gelatin microspheres induced angiogenesis in infarcted rabbits
Abstract
Background: Using several strategies, the stimulation of angiogenesis can alleviate the pathological complications of post-myocardial ischemia. Here, endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were pre-cultured inside the alginate/gelatin (Alg/Gel) microspheres in the presence of SDF-1α for 7 days, and their angiogenesis potential was monitored in infarcted rabbits.
Methods: The decapsulated cells were monitored in terms of cell dynamic growth and angiogenesis potential in vitro and after injection into ischemic myocardium in rabbits.
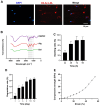
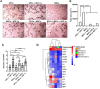
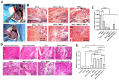
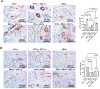
Results: Based on the data, 7-day incubation inside the Alg/Gel microspheres led to the stimulation of angiogenesis profile (Ang-1↑, -2↑, Tie-2↑), migration (MMP-2↑, and − 9↑), and autophagic response (Beclin-1↑, LC3↑, and p-62↓) in EPCs containing groups in the presence of SDF-1α. PCR array analysis revealed the expression of angiogenesis-related genes in the presence of SDF-1α. These features coincided with the stimulation of in vitro tubulogenesis properties in EPCs and EPCs + SDF-1α groups. The injection of cells from different groups into the infarcted rabbits led to the reduction of fibrotic area in ischemic myocardium in MSCs-bearing groups, and these effects were intensified in the presence of SDF-1α. Pre-treatment of EPCs and MSCs increased the recruited immune cells into the ischemic area within the myocardium. It was suggested that SDF-1α stimulated the local vascular density (CD31 capillaries, and α-SMA arterioles) in EPCs-bearing groups compared to MSCs and MSCs + SDF-1α groups.
Conclusions: These data indicate that pre-culture of EPCs and MSCs inside the Alg-based hydrogels can increase the regenerative potential of these cells, especially when exposed to stimulatory cytokines such as SDF-1α for the alleviation of ischemic changes.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12964-025-02301-0.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Endothelial progenitor cells; Mesenchymal stem cells; Myocardial infarction; Rabbits.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: In this study, the informed consent process was done by the children’s parents without any interference in the diagnosis process and therapeutic protocols, and samples were prepared according to the Declaration of Helsinki (1964). The current study was conducted according to the previously published guidelines and was registered as titled “Angiogenic properties of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells encapsulated inside alginate microspheres in a rabbit model of myocardial infarction” under an approval code of IR.TBZMED.REC.1399.125 from Research Ethics Committees of Vice-Chancellor in Research Affairs - Tabriz University of Medical Sciences on 2020-05-04, and by the Elite Researcher Grant Committee under award number [IR.NIMAD.REC.1400.151] from the National Institute for Medical Research Development (NIMAD), Tehran, Iran on 2021-11-30. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Juxtaposition of Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Endothelial Progenitor Cells Promoted Angiogenic Potential Inside Alginate-Gelatin Microspheres.Adv Pharm Bull. 2021 Jan;11(1):163-170. doi: 10.34172/apb.2021.017. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Adv Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 33747863 Free PMC article.
-
[Gelatin microspheres containing vascular endothelial growth factor enhances the efficacy of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in a swine model of myocardial infarction.].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2009 Mar;37(3):233-9. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19781147 Chinese.
-
Static and dynamic culture of human endothelial cells encapsulated inside alginate-gelatin microspheres.Microvasc Res. 2021 Sep;137:104174. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104174. Epub 2021 May 8. Microvasc Res. 2021. PMID: 33971187
-
Gelatin microspheres encapsulated with a nonpeptide angiogenic agent, ginsenoside Rg1, for intramyocardial injection in a rat model with infarcted myocardium.J Control Release. 2007 Jul 16;120(1-2):27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.04.005. Epub 2007 Apr 18. J Control Release. 2007. PMID: 17532519
-
Comparative effects of mesenchymal progenitor cells, endothelial progenitor cells, or their combination on myocardial infarct regeneration and cardiac function.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007 Nov;134(5):1249-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2007.07.028. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007. PMID: 17976457
References
-
- Yesmin S, et al. Knowledge regarding myocardial infarction (MI) among the nurses in dhaka, Bangladesh. Int J Sci Bus. 2022;14(1):108–15.
-
- Seslier T, Karakuş MÖ. In healthcare applications of machine learning algorithms for prediction of heart attacks. J Sci Reports-A (051):358–70.
-
- Jafari Sorkhdehi MM et al. Decellularization and characterization of camel pericardium as a new scaffold for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2024 May;32(4):194–199. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

