PAX Family, Master Regulator in Cancer
- PMID: 40506992
- PMCID: PMC12155527
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15111420
PAX Family, Master Regulator in Cancer
Abstract
PAX genes, known as master regulators, encode paired box (PAX) proteins that govern key processes in organ development and are widely expressed in normal tissues. Notably, PAX proteins also play a pivotal role in both promoting and suppressing tumorigenesis. They influence essential cellular functions such as survival, proliferation, fate determination, differentiation, invasion, metastasis, and the formation of oncogenic fusion proteins. In this review, we summarize the current understanding of these transcription factors. First, we provide a brief overview of their molecular structure, which underlies their classification into four subgroups. Then, we examine the expression patterns of each PAX gene across organ systems and explore their biological roles in the most relevant malignant neoplasms affecting human health. Additionally, we highlight their diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive significance in the context of cancer.
Keywords: EMT; PAX family; cancer; cell death; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
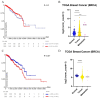
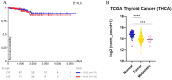
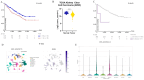
References
-
- Thompson B., Davidson E.A., Liu W., Nebert D.W., Bruford E.A., Zhao H., Dermitzakis E.T., Thompson D.C., Vasiliou V. Overview of PAX gene family: Analysis of human tissue-specific variant expression and involvement in human disease. Hum. Genet. 2021;140:381–400. doi: 10.1007/s00439-020-02212-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

