Mediterranean Diet Outcomes Across the Mother-Milk-Infant Triad: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40507029
- PMCID: PMC12157837
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17111760
Mediterranean Diet Outcomes Across the Mother-Milk-Infant Triad: A Narrative Review
Abstract
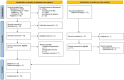
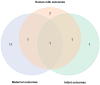
Nutrition plays a crucial role during pregnancy and lactation, influencing maternal and infant health, as well as human milk (HM) composition. The Mediterranean diet (MED) is recognized worldwide as a well-established healthy dietary pattern. This narrative review aims to integrate and summarize observational and interventional studies investigating the association between the MED and outcomes across the mother-milk-infant triad. A literature search was conducted in the Cochrane, Google Scholar, and PubMed databases, and 22 studies that met the eligibility criteria were included into review. The included studies were categorized into maternal outcomes (n = 13), HM composition outcomes (n = 9), and infant outcomes (n = 3). This narrative review suggests that adherence to the MED may be associated with maternal psychological health and well-being, postpartum weight loss, glucose metabolism, and the fatty acid profile of HM. Moreover, the included studies exhibited notable methodological differences that hindered direct comparisons and limited the generalizability of the findings. Future research should adopt an integrated and standardized methodology for assessing MED adherence, HM collection, and infant outcomes, considering the mother-human milk-infant triad.
Keywords: cardiometabolic health; fatty acids profile; infant growth; inflammatory biomarkers; maternal diet; postpartum depression; postpartum weight retention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Triad Mother-Breast Milk-Infant as Predictor of Future Health: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 2;13(2):486. doi: 10.3390/nu13020486. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33540672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal Mediterranean Diet During Lactation and Infant Growth.Breastfeed Med. 2024 Nov;19(11):848-856. doi: 10.1089/bfm.2024.0133. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Breastfeed Med. 2024. PMID: 39355969
-
Early infant adipose deposition is positively associated with the n-6 to n-3 fatty acid ratio in human milk independent of maternal BMI.Int J Obes (Lond). 2017 Apr;41(4):510-517. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2016.211. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Int J Obes (Lond). 2017. PMID: 27876761 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of maternal and infant omega-3 status at 3 months postpartum: findings from the APrON longitudinal cohort study.Am J Clin Nutr. 2025 Mar;121(3):629-642. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2025.01.002. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Am J Clin Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39788297 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of maternal diet on flavor transfer to amniotic fluid and breast milk and children's responses: a systematic review.Am J Clin Nutr. 2019 Mar 1;109(Suppl_7):1003S-1026S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy240. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30982867
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous