Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: Review of the Literature
- PMID: 40507410
- PMCID: PMC12155255
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14113649
Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: Review of the Literature
Abstract
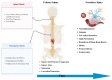
Traumatic spinal cord injury (tSCI) is a devastating neurological disorder with profound effects on physical, psychological, and mental abilities. tSCI affects all age groups, with a higher incidence in elderly patients. There are many causes of tSCI, with motor vehicle accidents (MVA) and falls being the most common. The pathophysiology of tSCI is quite complex and involves primary and secondary injury. The primary injury directly results from the mechanical forces that caused the injury. Secondary injury is caused by long-term changes caused by inflammation, immune changes, and the formation of free radicals. Numerous studies have explored various medical and surgical treatment options that help mitigate long-term damage caused by tSCI and help improve quality of life. Currently, there are no treatments for tSCI that can reverse spinal cord damage or fully restore motor and sensory functions. However, many pharmacological and non-pharmacological options are being studied in tSCI patients. This review will discuss the background, pathophysiology, and clinical presentation of tSCI while also providing a detailed analysis of the recent advancements in treatment options.
Keywords: ASIA score; SCI; neurological deficits; spinal cord injury; spinal injury; trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Safdarian M., Trinka E., Rahimi-Movaghar V., Thomschewski A., Aali A., Abady G.G., Abate S.M., Abd-Allah F., Abedi A., Adane D.E., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of spinal cord injury, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22:1026–1047. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00287-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources