Integrative Analysis of Drug Co-Prescriptions in Peritoneal Dialysis Reveals Molecular Targets and Novel Strategies for Intervention
- PMID: 40507495
- PMCID: PMC12155629
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14113733
Integrative Analysis of Drug Co-Prescriptions in Peritoneal Dialysis Reveals Molecular Targets and Novel Strategies for Intervention
Abstract
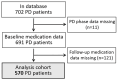
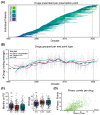
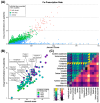
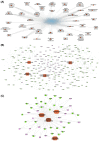
Background/Objectives: Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a renal replacement therapy for patients with kidney failure. Managing PD patients often involves addressing a complex interplay of comorbidities and complications, necessitating the use of multiple medications. This study aimed to systematically characterize commonly co-prescribed drugs in PD and to identify novel drug combinations that may target dysregulated molecular mechanisms associated with PD's pathophysiology. Methods: We analyzed clinical records from 702 PD patients spanning 30 years, encompassing over 5500 prescription points. Using network-based modeling techniques, we assessed drug co-prescription patterns, clinical outcomes, and longitudinal treatment trends. To explore potential drug repurposing opportunities, we constructed a molecular network model of PD based on a consolidated transcriptomics dataset and integrated this with drug-target interaction information. Results: We found commonly prescribed drugs such as furosemide, sucroferric oxyhydroxide, calcitriol, darbepoetin alfa, and aluminum hydroxide to be integral components of PD patient management, prescribed in over 30% of PD patients. The molecular-network-based approach found combinations of drugs like theophylline, fluoxetine, celecoxib, and amitriptyline to possibly have synergistic effects and to target dysregulated molecules of PD-related pathomechanisms. Two further distinct categories of drugs emerged as particularly interesting in our study: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which were found to modulate molecules implicated in peritoneal fibrosis, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors, which exhibit anti-fibrotic properties that are potentially useful for PD. Conclusions: This comprehensive exploration of drug co-prescriptions in the context of PD-related pathomechanisms provides valuable insights for opening future therapeutic strategies and identifying new targets for drug repurposing.
Keywords: biological networks; drug combination; drug repurposing; network analysis; peritoneal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
P.P. is an employee at Delta 4 GmbH. A.V. has consultancy agreements with Baxter and has received honoraria and travel grants unrelated to the current work from Baxter and Fresenius Medical Care (manufacturers of dialysis solutions), Fresenius Kabi, and Zytoprotec GmbH. K.K. is a co-founder of Delta 4 and part of Delta 4’s management team. R.H. and K.K. are former employees and consultants of Zytoprotec GmbH, a spin-off of the Medical University of Vienna that holds the patent “Carbohydrate-based peritoneal dialysis fluid comprising glutamine residue” (International Publication Number: WO 2008/106,702 A1) and the use patent “Peritoneal dialysis fluid comprising a GSK-3 inhibitor”.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription Patterns in Dialysis Patients: Differences Between Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis Patients and Opportunities for Deprescription.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2020 May 1;7:2054358120912652. doi: 10.1177/2054358120912652. eCollection 2020. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32426145 Free PMC article.
-
One-year efficacy and safety of the iron-based phosphate binder sucroferric oxyhydroxide in patients on peritoneal dialysis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017 Nov 1;32(11):1918-1926. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw460. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28339993 Clinical Trial.
-
Management of serum phosphorus over a 1-year follow-up in patients on peritoneal dialysis prescribed sucroferric oxyhydroxide as part of routine care: a retrospective analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Jun 17;25(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03633-8. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38886636 Free PMC article.
-
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy in Clinical Practice: Core Curriculum 2023.Am J Kidney Dis. 2023 Jan;81(1):100-109. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.07.004. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Am J Kidney Dis. 2023. PMID: 36208963 Review.
-
Current Insights into Cellular Determinants of Peritoneal Fibrosis in Peritoneal Dialysis: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 30;12(13):4401. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134401. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marques L., Costa B., Pereira M., Silva A., Santos J., Saldanha L., Silva I., Magalhaes P., Schmidt S., Vale N. Advancing Precision Medicine: A Review of Innovative In Silico Approaches for Drug Development, Clinical Pharmacology and Personalized Healthcare. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16:332. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030332. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang S., Kar S. Application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in early detection of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and drug-induced toxicity. Artif. Intell. Chem. 2023;1:100011. doi: 10.1016/j.aichem.2023.100011. - DOI
-
- Checa-Ros A., Locascio A., Steib N., Okojie O.J., Malte-Weier T., Bermudez V., D’Marco L. In silico medicine and -omics strategies in nephrology: Contributions and relevance to the diagnosis and prevention of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2025;44:49–57. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.23.334. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

